App Dev: Storing Application Data in Cloud Datastore - Python - GSP184
Table of Contents
Overview
Google Cloud Datastore is a NoSQL document database built for automatic scaling, high performance, and ease of application development. In this lab, you use Datastore to store application data for an online Quiz application. You also configure the application to retrieve from Datastore and display the data in the quiz.
The Quiz application skeleton has already been written. You clone the repository that contains the skeleton using Google Cloud Shell, review the code using the Cloud Shell editor, and view it using the Cloud Shell web preview feature. You then modify the code that stores data to use Cloud Datastore.
Objectives
In this lab, you learn how to perform the following tasks:
Harness Cloud Shell as your development environment
Preview the application
Update the application code to integrate Cloud Datastore
Task 1. Create a virtual environment
- Click on the Open Terminal icon.
Python virtual environments are used to isolate package installation from the system.
virtualenv -p python3 vrenv
- Activate the virtual environment:
source vrenv/bin/activate
Task 2. Prepare the Quiz application
The repository containing the Quiz application is located on GitHub.com. In this section, you use Cloud Shell to enter commands that clone the repository and run the application.
Clone source code in Cloud Shell
- Clone the repository for the class:
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/training-data-analyst
Configure and run the Quiz application
Change the working directory:
cd ~/training-data-analyst/courses/developingapps/python/datastore/startExport an environment variable,
GCLOUD_PROJECTthat references the Project ID:export GCLOUD_PROJECT=$DEVSHELL_PROJECT_IDNote: Project ID in Cloud Shell
While working in Cloud Shell, you will have access to the Project ID in the
$DEVSHELL_PROJECT_IDenvironment variable.Install the application dependencies and ignore the incompatibility warnings:
pip install -r requirements.txtRun the application:
python run_server.pyThe application is running when you see a message similar to the following:
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:8080/ (Press CTRL+C to quit) * Restarting with stat * Debugger is active! * Debugger PIN: 179-313-240
Review the Quiz application
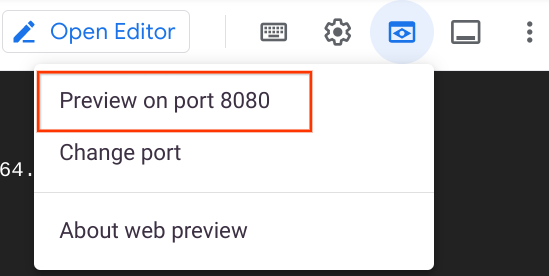
In Cloud Shell, click Web preview > Preview on port 8080 to preview the quiz application.
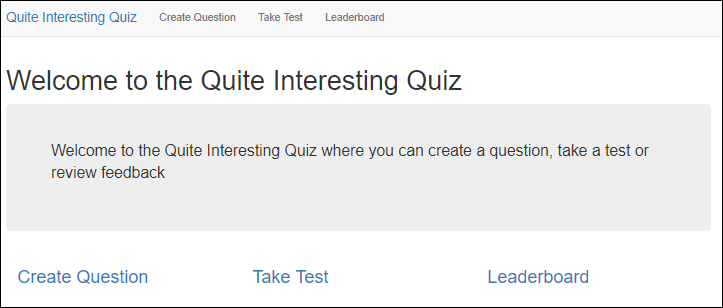
You should see the user interface for the web application. The three main parts to the application are:
Create Question
Take Test
Leaderboard
In the navigation bar, click Create Question.
You should see a simple form that contains textboxes for the question and answers with radio buttons to select the correct answer.
Note: Quiz authors can add questions in this part of the application. This part of the application is written as a server-side web application using the popular Python web application framework Flask.
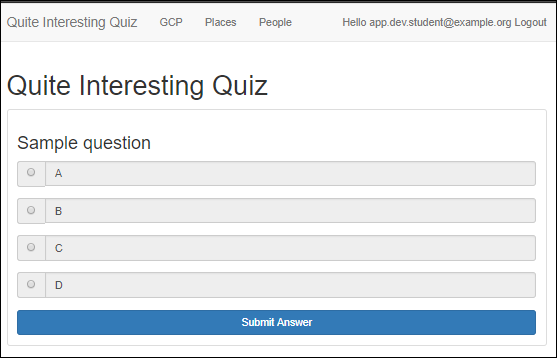
In the navigation bar, click Take Test, and then GCP to access the Google Cloud questions.
You should see a sample question.
Quiz takers answer questions in this part of the application.
Note: This part of the application is written as a client-side web application.
To return to the server-side application, click on the Quite Interesting Quiz link in the navigation bar.
Task 3. Examine the Quiz application code
In this lab, you'll view and edit files. You can use the shell editors that are installed on Cloud Shell, such as nano or vim or the Cloud Shell code editor.
This lab uses the Cloud Shell code editor to review the Quiz application code.
Review the Flask Web application
- Navigate to the
/training-data-analyst/courses/developingapps/python/datastore/startfolder using the file browser panel on the left side of the editor.
Note: Paths will be relative to this folder. This application is a standard Python application written using the popular Flask application framework.
Select the
...run_server.pyfile.This file contains the entrypoint for the application, and runs it on port 8080.
Select the
...quiz/_init_.py file.This file imports routes for the web application and REST API.
Select the
...quiz/webapp/questions.pyand...quiz/webapp/routes.pyfile.These files contain the routes that map URIs to handlers that display the form and collect form data posted by quiz authors in the web application.
Select the
...quiz/webapp/templatesfolder.This folder contains templates for the web application user interface using Jinja2 templates.
View the
...quiz/webapp/templates/add.htmlfile.This file contains the Jinja2 template for the Create Question form.
Notice how there is a select list to pick a quiz, textboxes where an author can enter the question and answers, and radio buttons to select the correct answer.
Select the
...quiz/api/api.pyfile.This file contains the handler that sends JSON data to students taking a test.
Select the
...quiz/gcp/datastore.pyfile.This is the file where you write Datastore code to save and load quiz questions to and from Cloud Datastore.
This module will be imported into the web application and API.
Task 4. Adding entities to Cloud Datastore
In this section, you write code to save form data in Cloud Datastore.
Note: Update code within the sections marked as follows:
# TODO
# END TODO
To maximize your learning, try to write the code without reference to the completed code block at the end of the section. In addition, review the code, inline comments, and related Datastore Client API documentation for Cloud Datastore.
Create an App Engine application to provision Cloud Datastore
Return to Cloud Shell and stop the application by pressing Ctrl+c.
To create an App Engine application in your project, use:
gcloud app create --region "europe-west4"
You'll see this message when the App Engine has been created:
Creating App Engine application in project [qwiklabs-gcp-f67238775c00cfaa] and region europe-west4....done.
Success! The app is now created. Please use `gcloud app deploy` to deploy your first app.
Note: You aren't using App Engine for your web application yet. However, Cloud Datastore requires you to create an App Engine application in your project.
Click Check my progress below to check your lab progress.
Create an App Engine application
Check my progress
Import and use the Python Datastore module
Open the
...quiz/gcp/datastore.pyfile in the Cloud Shell editor and add the Updated datastore.py code listed below to perform the following:Import the
osmodule.Use the os module to get the
GCLOUD_PROJECTenvironment variable.Import the
datastoremodule from thegoogle.cloudpackage.Declare a
datastore.Clientclient object nameddatastore_client.
Updated datastore.py
# TODO: Import the os module
import os
# END TODO
# TODO: Get the GCLOUD_PROJECT environment variable
project_id = os.getenv('GCLOUD_PROJECT')
# END TODO
from flask import current_app
# TODO: Import the datastore module from the google.cloud package
from google.cloud import datastore
# END TODO
# TODO: Create a Cloud Datastore client object
# The datastore client object requires the Project ID.
# Pass through the Project ID you looked up from the
# environment variable earlier
datastore_client = datastore.Client(project_id)
# END TODO
Write code to create a Cloud Datastore entity
- Still in
...quiz/gcp/datastore.py, move to thesave_question()function and remove the existingpassplaceholder statement. Add the following datastore.py - save_question() function code listed below to perform the following:
Use the Datastore client object to create a key for a Datastore entity whose kind is
'Question'.Use Datastore to create a Datastore question entity with the key.
Iterate over the items in the dictionary of values supplied from the Web application form.
In the body of the loop, assign each key and value to the Datastore entity object.
Use the Datastore client to save the data.
datastore.py - save_question() function
"""
Create and persist and entity for each question
The Datastore key is the equivalent of a primary key in a relational database.
There are two main ways of writing a key:
1. Specify the kind, and let Datastore generate a unique numeric id
2. Specify the kind and a unique string id
"""
def save_question(question):
# TODO: Create a key for a Datastore entity
# whose kind is Question
key = datastore_client.key('Question')
# END TODO
# TODO: Create a Datastore entity object using the key
q_entity = datastore.Entity(key=key)
# END TODO
# TODO: Iterate over the form values supplied to the function
for q_prop, q_val in question.items():
# END TODO
# TODO: Assign each key and value to the Datastore entity
q_entity[q_prop] = q_val
# END TODO
# TODO: Save the entity
datastore_client.put(q_entity)
# END TODO
- Save
datastore.py.
Run the application and create a Cloud Datastore entity
Save the
...quiz/gcp/datastore.pyfile and then return to the Cloud Shell command prompt.To run the application, execute the following command:
python run_server.py
In Cloud Shell, click Web preview > Preview on port 8080 to preview the quiz application.
Click Create Question.
Complete the form with the following values, and then click Save.
| Form Field | Value |
| Author | Your Name |
| Quiz | Google Cloud Platform |
| Title | Which company owns Google Cloud? |
| Answer 1 | Amazon |
| Answer 2 | Google (select the Answer 2 radio button!) |
| Answer 3 | IBM |
| Answer 4 | Microsoft |
You should return to the application home page.
Return to the Console, click Navigation menu > Datastore.
Select default database and click Entities.
You should see your new question!
Click Check my progress below to check your lab progress.
Create a Cloud Datastore entity
Check my progress
Retrieve Cloud Datastore entities
In this section, you write code to retrieve entity data from Cloud Datastore to view your question in the application.
Write code to retrieve Cloud Datastore entities
- In the code editor, in the
...quiz/gcp/datastore.pyfile, remove the code for thelist_entities(quiz, redact)function and replace it with a query that:
Retrieves Question entities for a specific quiz from Cloud Datastore.
Uses the Datastore client to fetch the query, and uses the returned data to create a list.
Enumerate the list of items, and promote each entity's Key identifier to a top level property.
Return the results.
- Replace this code:
"""
Returns a list of question entities for a given quiz
- filter by quiz name, defaulting to gcp
- no paging
- add in the entity key as the id property
- if redact is true, remove the correctAnswer property from each entity
"""
def list_entities(quiz='gcp', redact=True):
return [{'quiz':'gcp', 'title':'Sample question', 'answer1': 'A', 'answer2': 'B', 'answer3': 'C', 'answer4': 'D', 'correctAnswer': 1, 'author': 'Nigel'}]
"""
With this code:
"""
Returns a list of question entities for a given quiz
- filter by quiz name, defaulting to gcp
- no paging
- add in the entity key as the id property
- if redact is true, remove the correctAnswer property from each entity
"""
def list_entities(quiz='gcp', redact=True):
query = datastore_client.query(kind='Question')
query.add_filter('quiz', '=', quiz)
results =list(query.fetch())
for result in results:
result['id'] = result.key.id
if redact:
for result in results:
del result['correctAnswer']
return results
"""
- Save
datastore.py.
Run the application and test the Cloud Datastore query
Now to test if your question is retrieved from Datastore and loaded into your Quiz application.
- In Cloud Shell, press Ctrl+c to stop the application, then restart the application:
python run_server.py
Preview the quiz: If the browser running the quiz is still open, reload the browser. Otherwise, click Web preview > Preview on port 8080.
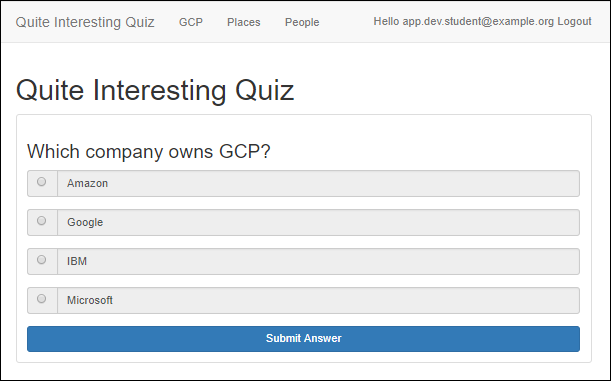
Click Take Test > GCP.
You should see the questions you created.
Solution of Lab
export REGION=

curl -LO raw.githubusercontent.com/quiccklabs/Labs_solutions/master/App%20Dev%20Storing%20Application%20Data%20in%20Cloud%20Datastore%20Python/quicklabgsp184.sh
sudo chmod +x quicklabgsp184.sh
./quicklabgsp184.sh