Table of Contents
Introduction
In a challenge lab you’re given a scenario and a set of tasks. Instead of following step-by-step instructions, you will use the skills learned from the labs in the course to figure out how to complete the tasks on your own! An automated scoring system (shown on this page) will provide feedback on whether you have completed your tasks correctly.
When you take a challenge lab, you will not be taught new Google Cloud concepts. You are expected to extend your learned skills, like changing default values and reading and researching error messages to fix your own mistakes.
To score 100% you must successfully complete all tasks within the time period!
This lab is recommended for students who have enrolled in the Build a Website on Google Cloud quest. Are you ready for the challenge?
Task 1. Download the monolith code and build your container
Log in to your new project and open up Cloud Shell.
First things first, you'll need to clone your team's git repo. There's a setup.sh script in the root directory of the project that you'll need to run to get your monolith container built up.
After running the
setup.shscript, ensure your Cloud Shell is running its latest version of nodeJS:
nvm install --lts
There will be a few different projects that can be built and pushed.
Push the monolith build (conveniently located in the
monolithdirectory) up to the Artifact Registry. There's a Dockerfile located in the~/monotlith-to-microservices/monolithfolder which you can use to build the application container.You will have to run Cloud Build (in that monolith folder) to build it, then push it up to Artifact Registry.
Name your artifact as follows:
Repo: gcr.io/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}
Image name:
fancy-monolith-580Image version: 1.0.0
Hint:
Make sure that you submit a build named fancy-monolith-580 with a version of "1.0.0".
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Download the monolith code and build your container
Check my progress
Task 2. Create a kubernetes cluster and deploy the application
Now that you have the image created and sitting in the Artifact Registry, it's time to create a cluster to deploy it to.
You've been told to deploy all of your resources in the europe-west4-b zone, so first you'll need to create a GKE cluster for it. Start with a 3 node cluster to begin with.
- Create your cluster as follows:
Cluster name:
fancy-prod-697Region:
europe-west4Node count: 3
Hint:
Make sure your cluster is named fancy-prod-697, and is in the running state in europe-west4.
Now that you've built up an image, and have a cluster up and running, it's time to deploy your application.
You'll need to deploy the image that you've built onto your cluster. This will get your application up and running, but it can't be accessed until you expose it to the outside world. Your team has told you that the application runs on port 8080, but you will need to expose this on a more consumer-friendly port 80.
- Create and expose your deployment as follows:
Cluster name:
fancy-prod-697Container name:
fancy-monolith-580Container version: 1.0.0
Application port: 8080
Externally accessible port: 80
Note: For purposes of this lab, exposure of the service has been simplified. Typically, you would use an API gateway to secure your public endpoints. Learn more about best practices in the Best practices for microservices Guide.
- Make note of the IP address that is assigned in the expose deployment operation. You should now be able to visit this IP address from your browser!
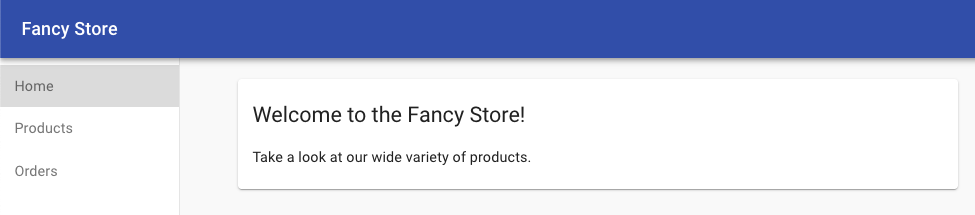
You should see the following:
Hint:
Make sure your deployment is named fancy-monolith-580, and that you have exposed the service on port 80, and mapped it to port 8080.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Create a kubernetes cluster and deploy the application
Check my progress
Now that you can build and deploy your Fancy Store monolith application, you're ready to start breaking it down into microservices!
Migrate monolith to microservices
Now that you have your existing monolith website running on GKE, you can start breaking each service into a microservice. Typically, a planning effort should take place on which services to break into smaller chunks, typically around specific parts of the application like business domain.
For the purposes of this Challenge, fast forward a bit and pretend that you have successfully broken out the monolith into a series of microservices: Orders, Products, and Frontend. Your code is ready, so now you've got to deploy your services.
Task 3. Create new microservices
There are 3 services that need to be broken out into their own containers. Since you are moving all of the services into containers, you need to track the following information for each service:
The root folder of the service (where you will build the container)
The repository you will upload the container to
The name & version of the container artifact
Create a containerized version of your microservices
Below is the set of services which need to be containerized.
- Navigate to the source roots mentioned below, and upload the artifacts that are created to the Artifact Registry with the metadata indicated:
| Orders Microservice | Service root folder: ~/monolith-to-microservices/microservices/src/orders |
| Products Microservice | Service root folder: ~/monolith-to-microservices/microservices/src/products |
- Once these microservices have been containerized, and their images uploaded to Artifact Registry, you should deploy and expose these services.
Hint: Make sure that you submit a build named fancy-orders-884 with a version of "1.0.0", AND a build named fancy-products-172 with a version of "1.0.0".
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Create a containerized version of orders and product Microservices
Check my progress
Task 4. Deploy the new microservices
Deploy these new containers following the same process that you followed for the fancy-monolith-580 monolith. Note that these services will be listening on different ports, so make note of the port mappings in the table below.
- Create and expose your deployments as follows:
| Orders Microservice | Cluster name: fancy-prod-697 |
| Products Microservice | Cluster name: fancy-prod-697 |
NOTE: Please make note of the IP address of both the Orders and Products services once they have been exposed, you will need them in future steps.
- You can verify that the deployments were successful and that the services have been exposed by going to the following URLs in your browser:
http://ORDERS_EXTERNAL_IP/api/orders
http://PRODUCTS_EXTERNAL_IP/api/products
You will see each service return a JSON string if the deployments were successful.
Hint: Make sure your deployments are named fancy-orders-884 and fancy-products-172, and that you see the services exposed on port 80.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Deploy the new microservices
Check my progress
Task 5. Configure and deploy the Frontend microservice
Now that you have extracted both the Orders and Products microservice, you need to configure the Frontend service to point to them, and get it deployed.
Reconfigure Frontend
- Use the
nanoeditor to replace the local URL with the IP address of the new Products microservices:
cd ~/monolith-to-microservices/react-app
nano .env
When the editor opens, your file should look like this:
REACT_APP_ORDERS_URL=http://localhost:8081/api/orders
REACT_APP_PRODUCTS_URL=http://localhost:8082/api/products
- Replace the
REACT_APP_PRODUCTS_URLto the new format while replacing with your Orders and Product microservice IP addresses so it matches below:
REACT_APP_ORDERS_URL=http://<ORDERS_IP_ADDRESS>/api/orders
REACT_APP_PRODUCTS_URL=http://<PRODUCTS_IP_ADDRESS>/api/products
Press CTRL+O, press ENTER, then CTRL+X to save the file in the
nanoeditor.Now rebuild the frontend app before containerizing it:
npm run build
Task 6. Create a containerized version of the Frontend microservice
With the Orders and Products microservices now containerized and deployed, and the Frontend service configured to point to them, the final step is to containerize and deploy the Frontend.
Use Cloud Build to package up the contents of the Frontend service and push it up to Artifact Registry.
Service root folder: ~/monolith-to-microservices/microservices/src/frontend
Repo: gcr.io/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}
Image name:
fancy-frontend-507Image version: 1.0.0
This process may take a few minutes, so be patient.
Hint: Make sure that you submit a build named fancy-frontend-507 with a version of "1.0.0".
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Create a containerized version of the Frontend microservice
Check my progress
Task 7. Deploy the Frontend microservice
Deploy this container following the same process that you followed for the "Orders" and "Products" microservices.
- Create and expose your deployment as follows:
Cluster name:
fancy-prod-697Container name:
fancy-frontend-507Container version: 1.0.0
Application port: 8080
Externally accessible port: 80
- You can verify that the deployment was successful and that the microservices have been properly exposed by hitting the following the IP address of the frontend service in your browser:?.
You will see the Fancy Store homepage, with links to the Products and Orders pages powered by your new microservices.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Deploy the Frontend microservice
Solution of Lab
export MONOLITH_IDENTIFIER=
export CLUSTER_NAME=
export ORDERS_IDENTIFIER=
export PRODUCTS_IDENTIFIER=
export FRONTEND_IDENTIFIER=

git clone https://github.com/googlecodelabs/monolith-to-microservices.git
cd ~/monolith-to-microservices
./setup.sh
cd ~/monolith-to-microservices/monolith
npm start
After this screen appears, the shortcut will be used (Ctrl + C)

gcloud services enable cloudbuild.googleapis.com
gcloud builds submit --tag gcr.io/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}/$MONOLITH_IDENTIFIER:1.0.0 .
gcloud config set compute/zone us-central1-a
gcloud services enable container.googleapis.com
gcloud container clusters create $CLUSTER_NAME --num-nodes 3
kubectl create deployment $MONOLITH_IDENTIFIER --image=gcr.io/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}/$MONOLITH_IDENTIFIER:1.0.0
kubectl expose deployment $MONOLITH_IDENTIFIER --type=LoadBalancer --port 80 --target-port 8080
cd ~/monolith-to-microservices/microservices/src/orders
gcloud builds submit --tag gcr.io/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}/$ORDERS_IDENTIFIER:1.0.0 .
cd ~/monolith-to-microservices/microservices/src/products
gcloud builds submit --tag gcr.io/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}/$PRODUCTS_IDENTIFIER:1.0.0 .
kubectl create deployment $ORDERS_IDENTIFIER --image=gcr.io/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}/$ORDERS_IDENTIFIER:1.0.0
kubectl expose deployment $ORDERS_IDENTIFIER --type=LoadBalancer --port 80 --target-port 8081
kubectl create deployment $PRODUCTS_IDENTIFIER --image=gcr.io/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}/$PRODUCTS_IDENTIFIER:1.0.0
kubectl expose deployment $PRODUCTS_IDENTIFIER --type=LoadBalancer --port 80 --target-port 8082
cd ~/monolith-to-microservices/react-app
cd ~/monolith-to-microservices/microservices/src/frontend
gcloud builds submit --tag gcr.io/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}/$FRONTEND_IDENTIFIER:1.0.0 .
kubectl create deployment $FRONTEND_IDENTIFIER --image=gcr.io/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}/$FRONTEND_IDENTIFIER:1.0.0
kubectl expose deployment $FRONTEND_IDENTIFIER --type=LoadBalancer --port 80 --target-port 8080