Table of Contents
Overview
Serverless computing on Google Cloud lets you develop and deploy highly scalable applications on a fully managed serverless platform. Services are automatically scaled up and down depending on traffic.
Service integration lets you easily integrate your services in an asynchronous, loosely coupled manner, allowing rapid innovation. Eventarc lets you build event-driven architectures without requiring infrastructure management. Workflows lets you easily build reliable applications by orchestrating services and APIs. Cloud Scheduler is a fully managed cron job service for scheduling your workloads. Cloud Tasks is a fully managed service for creating distributed task queues. Eventarc, Workflows, Cloud Scheduler, and Cloud Tasks help you integrate your services while maintaining observability, reliability, and security.
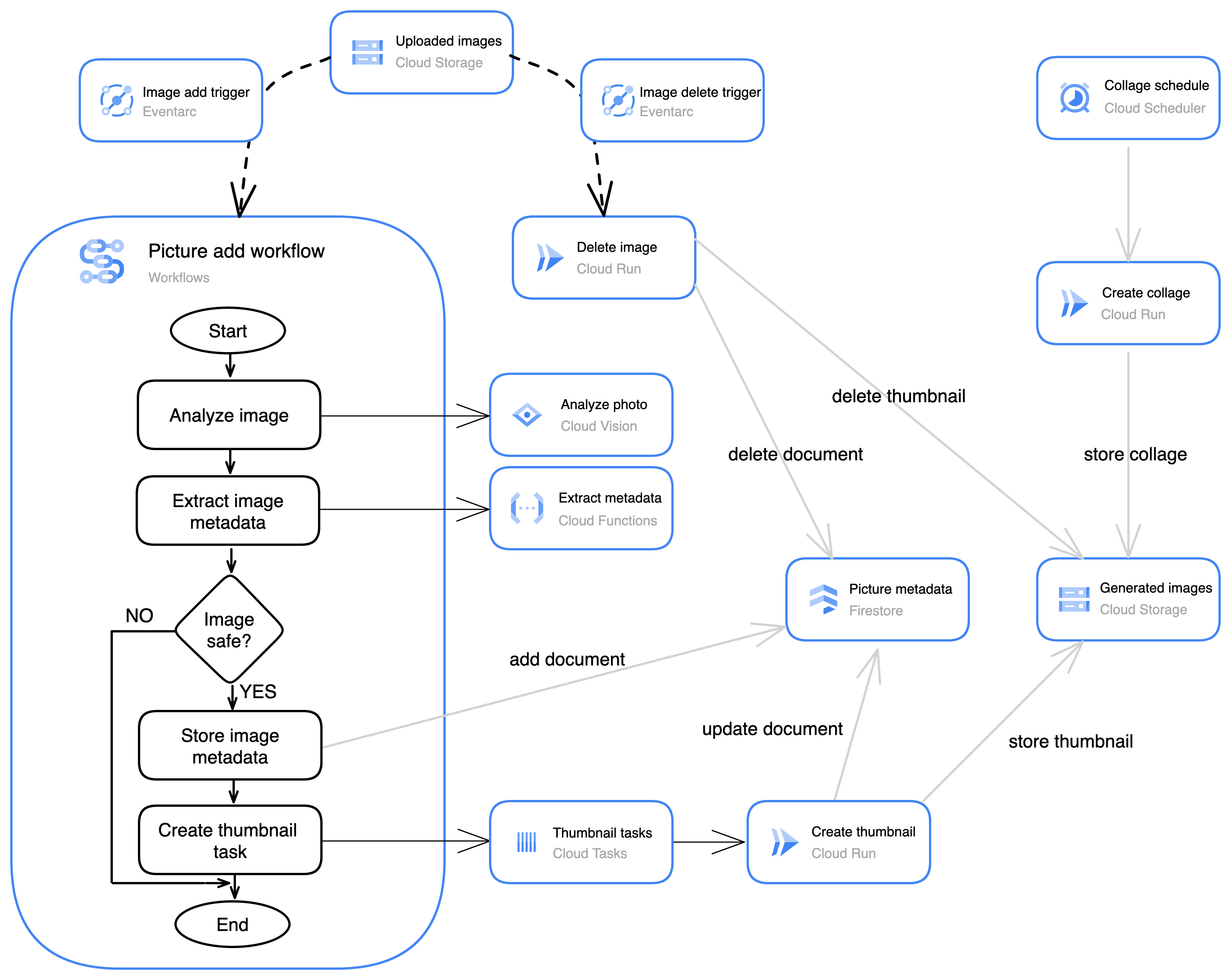
In this lab, you use Workflows to create a workflow that manages the process of creating thumbnails and extracting metadata from incoming images. Eventarc detects when an image is uploaded to a Cloud Storage bucket and starts an execution of your workflow.
The workflow calls the Cloud Vision API to analyze the uploaded photo. Cloud Vision determines whether the image is safe, detects text in the image, and provides labels for the image content. The vision data is extracted using a custom function created in Cloud Functions. The extracted data is saved in Firestore, Google Cloud's fully managed serverless document database. The workflow also uses Cloud Tasks to queue a task for creating a thumbnail.
Cloud Build is used to build three services that are deployed in Cloud Run, a serverless platform for running containerized services. One of these services creates a thumbnail in response to the task created by the workflow.
The second service creates a photo collage of the most recent images. The collage service runs on a schedule created in Cloud Scheduler.
The third service is triggered by Eventarc when an image is deleted from the Cloud Storage bucket. This service will remove the metadata and thumbnail image for the deleted image.
What you will learn
In this lab, you will learn to:
Asynchronously trigger services and workflows using Eventarc.
Orchestrate services and APIs using Workflows.
Manage a distributed task queue using Cloud Tasks.
Execute services on a schedule using Cloud Scheduler.
Setup and requirements
Before you click the Start Lab button
Note: Read these instructions.
Labs are timed and you cannot pause them. The timer, which starts when you click Start Lab, shows how long Google Cloud resources will be made available to you.
This Qwiklabs hands-on lab lets you do the lab activities yourself in a real cloud environment, not in a simulation or demo environment. It does so by giving you new, temporary credentials that you use to sign in and access Google Cloud for the duration of the lab.
What you need
To complete this lab, you need:
Access to a standard internet browser (Chrome browser recommended).
Time to complete the lab.
Note: If you already have your own personal Google Cloud account or project, do not use it for this lab.
Note: If you are using a Pixelbook, open an Incognito window to run this lab.
How to start your lab and sign in to the Console
Click the Start Lab button. If you need to pay for the lab, a pop-up opens for you to select your payment method. On the left is a panel populated with the temporary credentials that you must use for this lab.
Copy the username, and then click Open Google Console. The lab spins up resources, and then opens another tab that shows the Choose an account page.
Note: Open the tabs in separate windows, side-by-side.
On the Choose an account page, click Use Another Account. The Sign in page opens.
Paste the username that you copied from the Connection Details panel. Then copy and paste the password.
Note: You must use the credentials from the Connection Details panel. Do not use your Google Cloud Skills Boost credentials. If you have your own Google Cloud account, do not use it for this lab (avoids incurring charges).
- Click through the subsequent pages:
Accept the terms and conditions.
Do not add recovery options or two-factor authentication (because this is a temporary account).
Do not sign up for free trials.
After a few moments, the Cloud console opens in this tab.
Note: You can view the menu with a list of Google Cloud Products and Services by clicking the Navigation menu at the top-left.
Activate Google Cloud Shell
Google Cloud Shell is a virtual machine that is loaded with development tools. It offers a persistent 5GB home directory and runs on the Google Cloud.
Google Cloud Shell provides command-line access to your Google Cloud resources.
In Cloud console, on the top right toolbar, click the Open Cloud Shell button.
Click Continue.
It takes a few moments to provision and connect to the environment. When you are connected, you are already authenticated, and the project is set to your PROJECT_ID. For example:
gcloud is the command-line tool for Google Cloud. It comes pre-installed on Cloud Shell and supports tab-completion.
- You can list the active account name with this command:
gcloud auth list
Output:
Credentialed accounts:
- @.com (active)
Example output:
Credentialed accounts:
- google1623327_student@qwiklabs.net
- You can list the project ID with this command:
gcloud config list project
Output:
[core]
project =
Example output:
[core]
project = qwiklabs-gcp-44776a13dea667a6
Note: Full documentation of gcloud is available in the gcloud CLI overview guide .
Task 1. Enable APIs and create Cloud Storage buckets
In this task, you enable required APIs. You also create two buckets in Cloud Storage: one for uploading images, and one to store images generated by your application.
Enable APIs
To enable the required APIs, run the following command:
gcloud services enable \ workflows.googleapis.com \ workflowexecutions.googleapis.com \ eventarc.googleapis.com \ tasks.googleapis.com \ cloudscheduler.googleapis.com \ storage.googleapis.com \ vision.googleapis.com \ run.googleapis.com \ cloudfunctions.googleapis.com \ firestore.googleapis.com \ appengine.googleapis.com \ cloudbuild.googleapis.com \ artifactregistry.googleapis.comThis application uses several Google Cloud services, and you must enable each of the APIs for these services.
The APIs being enabled:
The Workflows API manages the definitions of workflows. A workflow will run the primary process when a new image is uploaded.
The Workflows Executions API manages executions of workflows.
The Eventarc API manages Eventarc configuration. Eventarc will be used to detect images added to and deleted from a Cloud Storage bucket.
The Cloud Tasks API creates and manages distributed tasks. A task will be created by the workflow to cause a thumbnail to be created.
The Cloud Scheduler API creates and manages scheduled cron jobs. A scheduled job will be used to create a collage for the latest images.
The Cloud Storage API creates and manages Cloud Storage buckets and objects.
The Cloud Vision API enables access to Google's machine learning vision features.
The Cloud Run API creates and manages Cloud Run services. Cloud Run services are provided to create a thumbnail, delete an image, and create a collage.
The Cloud Functions API creates and manages functions. A function is used to extract information from the Cloud Vision response.
The Firestore API creates and manages Firestore databases.
The App Engine API creates and manages App Engine applications. The App Engine API is required to enable Firestore.
The Cloud Build API manages application builds.
The Artifact Registry API manages build artifacts and registries.
Create Cloud Storage buckets
In Cloud Shell, create a Cloud Storage bucket for uploading images:
export UPLOAD_BUCKET=uploaded-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} gcloud storage buckets create \ --location=us-west1 gs://${UPLOAD_BUCKET} gcloud storage buckets update \ gs://${UPLOAD_BUCKET} --uniform-bucket-level-access gcloud storage buckets add-iam-policy-binding \ gs://${UPLOAD_BUCKET} \ --member=allUsers --role=roles/storage.objectViewerThese commands create a public regional bucket with uniform access. Each time an image is copied to the bucket, a workflow will be started to analyze the photo and store the metadata and a thumbnail image.
Create a second Cloud Storage bucket for images generated by the image applications:
export GENERATED_BUCKET=generated-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} gcloud storage buckets create \ --location=us-west1 gs://${GENERATED_BUCKET} gcloud storage buckets update \ gs://${GENERATED_BUCKET} --uniform-bucket-level-access gcloud storage buckets add-iam-policy-binding \ gs://${GENERATED_BUCKET} \ --member=allUsers --role=roles/storage.objectViewerIn the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu (), navigate to Cloud Storage > Buckets.
The two buckets that you created are shown.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Create Cloud Storage buckets
Check my progress
Task 2. Create the Firestore database
In this task, you create the Firestore database that will store image metadata.
Create the database
To create the Firestore database, in Cloud Shell, run the following command:
export FIRESTORE_LOCATION=us-west1 gcloud firestore databases create \ --location=${FIRESTORE_LOCATION} \ --type=firestore-nativeA Firestore collection named images will be used to store image metadata. The collage service will search the database to find the most recent images with thumbnails to create the collage.
After the database is created, you must create an index to support this search.
Create the Firestore composite index
A Firestore composite index is used when you need a single query to reference multiple fields.
To create the composite index, run the following command:
gcloud firestore indexes composite create \ --collection-group=images \ --field-config field-path=thumbnail,order=descending \ --field-config field-path=created,order=descending \ --asyncThis index will let the collage service find the most recent images that have thumbnails.
The --async parameter indicates that you do not want to wait for the operation to complete.
In the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu (), navigate to More Products > Databases > Firestore > Indexes.
You should see that the index on the images collection is being created.
Creating the search index may take several minutes. You can continue with the lab before the index creation is completed.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Create the Firestore database and composite index
Check my progress
Task 3. Create the thumbnail task queue
In this task, you create a Cloud Tasks queue for requesting thumbnail creation by the create-thumbnail service.
To create the task queue, in Cloud Shell, enter the following command:
export QUEUE_REGION=us-west1 gcloud tasks queues create thumbnail-task-queue \ --location=${QUEUE_REGION}In the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu (), navigate to More Products > Integration Services > Cloud Tasks.
The queue named thumbnail-task-queue has been created.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Create the Cloud Tasks queue
Check my progress
Task 4. Deploy the Cloud Run services
In this task, you build and deploy the Cloud Run services that will be used by the image application.
Clone the source code repository
In Cloud Shell, clone the git repository:
git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/training-data-analystCreate a soft link shortcut to the root directory for this lab:
ln -s ~/training-data-analyst/courses/orchestration-and-choreography/lab1 ~/code
Create a repository in Artifact Registry
Artifact Registry is the next generation of Container Registry. You can store build artifacts inside an Artifact Registry repository.
To create an Artifact Registry repository for Docker images, in Cloud Shell, run the following command:
export REPO_NAME=image-app-repo export REPO_REGION=us-west1 gcloud artifacts repositories create ${REPO_NAME} \ --location=${REPO_REGION} --repository-format=docker
Build and deploy the create-thumbnail service
The thumbnail service creates a thumbnail for an uploaded image and stores it in the generated-images bucket.
In Cloud Shell, click Open Editor.
In Cloud Editor, click Explorer (), and then click Open Folder.
Click code, and then click OK.
Navigate to
~/code/cloud-run/create-thumbnailand examine the files for the create-thumbnail service.The directory contains three files:
package.json holds metadata relevant to building your Node.js application. It defines the command that starts the application (node index.js) and specifies the versions of packages used by the code.
Dockerfile specifies the starting image (node:16-slim) and contains the list of commands that are run to build the container image that will host our service. The installation includes installing Imagemagick, which will be used to create thumbnail images from uploaded images.
index.js contains the code for the service.
Click Open Terminal.
To build the create-thumbnail service Docker image using Cloud Build, in Cloud Shell, run the following commands:
export REPO_NAME=image-app-repo export REPO_REGION=us-west1 export THUMBNAIL_SERVICE_NAME=create-thumbnail cd ~/code/cloud-run/create-thumbnail gcloud builds submit \ . \ --tag ${REPO_REGION}-docker.pkg.dev/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}/${REPO_NAME}/${THUMBNAIL_SERVICE_NAME}The service is built and stored in the Artifact Registry repository.
To deploy the service using Cloud Run, in Cloud Shell, run the following commands:
export REPO_NAME=image-app-repo export REPO_REGION=us-west1 export THUMBNAIL_SERVICE_REGION=us-west1 export THUMBNAIL_SERVICE_NAME=create-thumbnail export GENERATED_IMAGES_BUCKET=generated-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} cd ~/code/cloud-run/create-thumbnail gcloud config set run/region ${THUMBNAIL_SERVICE_REGION} gcloud config set run/platform managed gcloud run deploy ${THUMBNAIL_SERVICE_NAME} \ --image ${REPO_REGION}-docker.pkg.dev/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}/${REPO_NAME}/${THUMBNAIL_SERVICE_NAME} \ --no-allow-unauthenticated \ --memory=1Gi \ --max-instances=1 \ --update-env-vars GENERATED_IMAGES_BUCKET=${GENERATED_IMAGES_BUCKET}The generated-images bucket name is passed to the application using an environment variable.
Build and deploy the collage service
The collage service combines the most recently uploaded images into a collage and stores the collage in the generated images bucket.
In Cloud Shell, click Open Editor.
In Cloud Editor, navigate to
~/code/cloud-run/create-collageand examine the files for the create-collage service.This directory contains three files: package.json, index.js, and Dockerfile.
Click Open Terminal.
To build and deploy the create-collage service Docker image, in Cloud Shell, run the following commands:
export REPO_NAME=image-app-repo export REPO_REGION=us-west1 export COLLAGE_SERVICE_REGION=us-west1 export COLLAGE_SERVICE_NAME=create-collage export GENERATED_IMAGES_BUCKET=generated-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} cd ~/code/cloud-run/create-collage gcloud builds submit \ . \ --tag ${REPO_REGION}-docker.pkg.dev/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}/${REPO_NAME}/${COLLAGE_SERVICE_NAME} gcloud config set run/region ${COLLAGE_SERVICE_REGION} gcloud config set run/platform managed gcloud run deploy ${COLLAGE_SERVICE_NAME} \ --image ${REPO_REGION}-docker.pkg.dev/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}/${REPO_NAME}/${COLLAGE_SERVICE_NAME} \ --no-allow-unauthenticated \ --memory=1Gi \ --max-instances=1 \ --update-env-vars GENERATED_IMAGES_BUCKET=${GENERATED_IMAGES_BUCKET}
Build and deploy the delete image service
The delete image service removes the thumbnail image from the generated images bucket and deletes the image metadata from the database.
In Cloud Shell, click Open Editor.
In Cloud Editor, navigate to
~/code/cloud-run/delete-imageand examine the files for the delete-image service.This directory only contains two files: package.json and index.js. There's no Dockerfile.
Instead of building and publishing the container manually, this lab relies on Google Cloud Buildpacks to automatically build the container.
Also note that the service parses the request as a CloudEvent. Eventarc sends events using the standard CloudEvent format.
Click Open Terminal.
To build and deploy the delete-image service to Cloud Run using Google Cloud Buildpacks, in Cloud Shell, run the following commands:
export DELETE_SERVICE_REGION=us-west1 export DELETE_SERVICE_NAME=delete-image export GENERATED_IMAGES_BUCKET=generated-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} cd ~/code/cloud-run/delete-image gcloud config set run/region ${DELETE_SERVICE_REGION} gcloud config set run/platform managed gcloud run deploy ${DELETE_SERVICE_NAME} \ --source . \ --no-allow-unauthenticated \ --max-instances=1 \ --update-env-vars GENERATED_IMAGES_BUCKET=${GENERATED_IMAGES_BUCKET}gcloud run deploy warns that an Artifact Registry Docker repository must be created for images created by Google Cloud Buildpacks.
When asked if you want to continue, enter
Y.
Examine the artifact repositories and Cloud Run services
In the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu (), navigate to More Products > CI/CD > Artifact Registry > Repositories.
The repository you created (image-app-repo) and the repository created by Google Cloud Buildpacks (cloud-run-source-deploy) are in the Artifact Registry.
Click image-app-repo.
Stored in image-app-repo are the Docker images you just built for the create-collage and create-thumbnail services.
Return to Artifact Registry > Repositories, and then click cloud-run-source-deploy.
The repository contains the delete-image Docker image that was automatically created by Google Cloud Buildpacks.
In the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu (), navigate to Cloud Run > Services.
All three services have been deployed.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Create the repository and deploy the Cloud Run services
Check my progress
Task 5. Create a function to parse the Cloud Vision response
In this task, you create a Cloud Function to parse the image data returned by the Cloud Vision API.
In Cloud Shell, click Open Editor.
In Cloud Editor, navigate to
~/code/cloud-functions/extract-image-metadataand examine the files for the extract-image-metadata function.The Node.js service contains index.js and package.json files. Cloud Functions automatically uses Buildpacks to create the container, so no Dockerfile is required.
Click Open Terminal.
To deploy the function, in Cloud Shell, run the following command:
export EXTRACT_FUNCTION_REGION=us-west1 export EXTRACT_FUNCTION_NAME=extract-image-metadata cd ~/code/cloud-functions/${EXTRACT_FUNCTION_NAME} gcloud config set functions/region ${EXTRACT_FUNCTION_REGION} gcloud functions deploy ${EXTRACT_FUNCTION_NAME} \ --source . \ --runtime=nodejs18 \ --entry-point=extract_image_metadata \ --trigger-http \ --no-allow-unauthenticatedNote: If the deploy indicates that repository metadata could not be retrieved, try a few more times until the function deployment works.
In the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu (), navigate to Serverless > Cloud Functions.
The extract-image-metadata function has been deployed.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Create the function to parse the Cloud Vision response
Check my progress
Task 6. Create the workflow
In this task, you create a workflow to orchestrate your service and API calls.
In Cloud Shell, click Open Editor.
In Cloud Editor, navigate to
~/code/code/workflowsand examine the image-add-workflow.yaml YAML file.The workflow specifies a series of steps to be performed when the workflow is initiated. Here are the non-logging steps:
init assigns variables that will be used in the workflow. bucket and filename are populated with values passed by Eventarc when the workflow is called. projectId gets the project ID value from an environment variable that is automatically populated for a workflow.
imageAnalysisCall calls the Cloud Vision API to analyze the uploaded image.
extractImageMetadata calls a Cloud Function to extract the important information out of the Cloud Vision API call response.
checkSafety exits the workflow when the Cloud Vision API determines that the image is unsafe.
storeMetadata calls the Firestore API to store the image metadata.
getThumbnailService calls a Cloud Run connector to find the URL of the create-thumbnail Cloud Run service.
queueThumbnail uses a Cloud Tasks connector to create a task to asynchronously call the thumbnail service.
completed ends the workflow, returning the identifier of the workflow execution.
Click Open Terminal.
To create a service account for the workflow identity and add some basic permissions, run the following commands:
export WORKFLOWS_SA=workflows-sa gcloud iam service-accounts create ${WORKFLOWS_SA} gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} \ --member="serviceAccount:${WORKFLOWS_SA}@${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/datastore.user" gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} \ --member="serviceAccount:${WORKFLOWS_SA}@${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/cloudtasks.enqueuer" gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} \ --member="serviceAccount:${WORKFLOWS_SA}@${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/logging.logWriter" gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} \ --member="serviceAccount:${WORKFLOWS_SA}@${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/iam.serviceAccountUser"The roles permit the following functionality:
roles/datastore.user lets the workflow write documents to Firestore.
roles/cloudtasks.enqueuer lets the workflow create a Cloud Task.
roles/logging.logWriter lets the workflow log variables to Cloud Logging.
roles/iam.serviceAccountUser lets the service account impersonate another service account, so Cloud Tasks can send the request using the workflow service account identity.
To add permissions to call the function and Cloud Run service, run the following commands:
export WORKFLOWS_SA=workflows-sa export THUMBNAIL_SERVICE_NAME=create-thumbnail export THUMBNAIL_SERVICE_REGION=us-west1 export EXTRACT_FUNCTION_NAME=extract-image-metadata gcloud functions add-iam-policy-binding ${EXTRACT_FUNCTION_NAME} \ --member="serviceAccount:${WORKFLOWS_SA}@${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/cloudfunctions.invoker" gcloud run services add-iam-policy-binding ${THUMBNAIL_SERVICE_NAME} \ --region=${THUMBNAIL_SERVICE_REGION} \ --member="serviceAccount:${WORKFLOWS_SA}@${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/run.viewer" gcloud run services add-iam-policy-binding ${THUMBNAIL_SERVICE_NAME} \ --region=${THUMBNAIL_SERVICE_REGION} \ --member="serviceAccount:${WORKFLOWS_SA}@${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/run.invoker"These additional roles permit the following functionality:
roles/cloudfunctions.invoker lets the workflow call the function that extracts the metadata from the Cloud Vision response.
roles/run.viewer lets the workflow query the thumbnail service details.
roles/run.invoker lets the workflow service account call the thumbnail service. The service account will be used by Cloud Tasks when calling the service.
To deploy the workflow, run the following command:
export WORKFLOW_NAME=image-add-workflow export WORKFLOW_REGION=us-west1 export WORKFLOWS_SA=workflows-sa cd ~/code/workflows gcloud workflows deploy ${WORKFLOW_NAME} \ --source=${WORKFLOW_NAME}.yaml \ --location=${WORKFLOW_REGION} \ --service-account="${WORKFLOWS_SA}@${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com"In the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu (), navigate to More Products > Integration Services > Workflows > Workflows.
Click image-add-workflow, and then click Source.
The left pane displays the code for the workflow, and the right pane displays a flow visualization for the steps of the workflow.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Create the workflow
Check my progress
Task 7. Create an Eventarc trigger to start the workflow
In this task, you will create an Eventarc trigger that runs the workflow when a file is added to the uploaded-images bucket.
To create a service account for the workflow trigger, and grant it the necessary permissions, in Cloud Shell, run the following command:
export WORKFLOW_TRIGGER_SA=workflow-trigger-sa gcloud iam service-accounts create ${WORKFLOW_TRIGGER_SA} gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} \ --member="serviceAccount:${WORKFLOW_TRIGGER_SA}@${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/workflows.invoker" gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} \ --member "serviceAccount:${WORKFLOW_TRIGGER_SA}@${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/eventarc.eventReceiver"These commands create a service account named workflow-trigger-sa, and add roles to receive events and invoke workflows.
To grant the Cloud Storage service account permission to create events, run the following command:
export CLOUD_STORAGE_SA="$(gcloud storage service-agent)" gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} \ --member="serviceAccount:${CLOUD_STORAGE_SA}" \ --role="roles/pubsub.publisher"These commands retrieve the Cloud Storage service account and add the permission to publish Pub/Sub events.
To create the trigger, run the following command:
export WORKFLOW_TRIGGER_REGION=us-west1 export WORKFLOW_NAME=image-add-workflow export WORKFLOW_REGION=us-west1 export UPLOAD_BUCKET=uploaded-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} export WORKFLOW_TRIGGER_SA=workflow-trigger-sa gcloud eventarc triggers create image-add-trigger \ --location=${WORKFLOW_TRIGGER_REGION} \ --destination-workflow=${WORKFLOW_NAME} \ --destination-workflow-location=${WORKFLOW_REGION} \ --event-filters="type=google.cloud.storage.object.v1.finalized" \ --event-filters="bucket=${UPLOAD_BUCKET}" \ --service-account="${WORKFLOW_TRIGGER_SA}@${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com"This trigger will call the workflow whenever a file is written to the uploaded-images bucket.
If you receive a permissions propagation error when creating the trigger, a permission may not have been propagated to Eventarc yet. Retrying the trigger creation once or twice should work.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Create the Eventarc trigger to start the workflow
Check my progress
Task 8. Test the add image workflow
In this task, you test the steps that occur when an image is added to the uploaded-images bucket.
To upload an image to the uploaded-images bucket, run the following commands:
export UPLOAD_BUCKET=uploaded-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} export IMAGE_NAME=neon.jpg gcloud storage cp ~/code/images/${IMAGE_NAME} gs://${UPLOAD_BUCKET}When the upload finishes, Eventarc detects the upload and starts the workflow.
In the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu (), navigate to More Products > Integration Services > Workflows > Workflows.
Click image-add-workflow, and then click Executions.
Click the execution ID to open the Execution Details page.
This page shows the details of the workflow execution.
The Input pane shows the contents of the Cloud Storage event that was sent by the Eventarc trigger.
The Output pane shows the values that were returned at the end of the workflow.
The Logs pane shows log entries created by the workflow.
In the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu (), navigate to Serverless > Cloud Functions, and then click extract-image-metadata.
This dashboard shows details about the function used to extract the information from the Cloud Vision response.
Click the Logs tab.
Logged data from the function execution is found here. The labels and text for the image were logged.
In the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu (), navigate to More Products > Databases > Firestore, and then click (default).
The images collection should show a document named neon.jpg that was written by the workflow. The labels attached to the image and the text found within the image are shown.
In the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu (), navigate to Cloud Run > Services, and then click create-thumbnail.
This dashboard shows information about the create-thumbnail service.
Click the Logs tab.
Data logged from the service execution is found here.
In Cloud Shell, run the following commands:
export UPLOAD_BUCKET=uploaded-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} export GENERATED_BUCKET=generated-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} export IMAGE_NAME=neon.jpg echo "uploaded image: https://storage.googleapis.com/${UPLOAD_BUCKET}/${IMAGE_NAME}" echo "generated image: https://storage.googleapis.com/${GENERATED_BUCKET}/${IMAGE_NAME}" echo "Listing of generated-images bucket:" gcloud storage ls gs://${GENERATED_BUCKET}The generated-images bucket should have a thumbnail created by the create-thumbnail service. You can click the links within Cloud Shell to open a new tab and see the uploaded and generated images.
It may take a short time before the generated image shows up in the bucket and listing.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Test the add image workflow
Check my progress
Task 9. Add a scheduled job to create a collage
In this task, you will create a Cloud Scheduler job to periodically create a collage of the most recently uploaded photos.
Upload images
To upload more images to the uploaded-images bucket, run the following commands:
export UPLOAD_BUCKET=uploaded-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} gcloud storage cp ~/code/images/alley.jpg \ gs://${UPLOAD_BUCKET} gcloud storage cp ~/code/images/desktop.jpg \ gs://${UPLOAD_BUCKET} gcloud storage cp ~/code/images/rainbow.jpg \ gs://${UPLOAD_BUCKET} gcloud storage cp ~/code/images/vegas.jpg \ gs://${UPLOAD_BUCKET}The workflow will run for each image, resulting in a thumbnail for each image.
To create a service account for calling the create-collage service, run the following commands:
export COLLAGE_SCHED_SA=collage-schedule-sa export COLLAGE_SERVICE=create-collage export COLLAGE_SERVICE_REGION=us-west1 gcloud iam service-accounts create ${COLLAGE_SCHED_SA} gcloud run services add-iam-policy-binding ${COLLAGE_SERVICE} \ --region=${COLLAGE_SERVICE_REGION} \ --member="serviceAccount:${COLLAGE_SCHED_SA}@${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/run.invoker"To retrieve the service URL for the create-collage service, in Cloud Shell, run the following command:
export SERVICE_REGION=us-west1 export SERVICE_NAME=create-collage gcloud run services describe ${SERVICE_NAME} \ --platform managed \ --region ${SERVICE_REGION} \ --format 'value(status.url)'Copy the URL into the clipboard. You will need this URL when creating the scheduled job.
In the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu (), navigate to More Products > Integration Services > Cloud Scheduler, and then click +Create Job.
Specify the following schedule settings:
| Property | Value | | --- | --- | | Name | collage-schedule | | Region | select
us-west1| | Frequency | * | | Timezone | search for UTC and then select Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) |The frequency specifies the schedule in unix-cron format. * specifies that the job will run once a minute.
The frequency of once a minute is chosen for ease of testing.
Click Continue, and then select the Target type of HTTP.
Specify the following execution settings:
| Property | Value | | --- | --- | | URL | paste the create-collage service URL | | HTTP method | select POST | | Auth header | select Add OIDC token | | Service account | select collage-schedule-sa | | Audience | paste the create-collage service URL |
Click Continue, and then click Create.
The collage-schedule job is displayed on the Cloud Scheduler Jobs page.
The job should run within a minute.
Click Refresh until the collage-schedule job shows a check mark, indicating success.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Add a scheduled job to create the collage
Check my progress
In Cloud Shell, run the following commands:
export GENERATED_BUCKET=generated-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} export IMAGE_NAME=collage.png echo "generated collage: https://storage.googleapis.com/${GENERATED_BUCKET}/${IMAGE_NAME}" echo "Listing of generated-images bucket:" gcloud storage ls gs://${GENERATED_BUCKET}The generated-images bucket should now include the collage.png file. You can click the "generated collage" link within Cloud Shell to open a new tab and see the collage.
A file copied into Cloud Storage is available immediately after the file upload process completes, so the link should work immediately after the scheduled job completes. When you list the bucket contents, the file may not show up until a short time later.
Task 10. Trigger a service to delete image files and metadata
In this task, you will create an Eventarc trigger to remove the associated thumbnail image and remove the Firestore document when an image is deleted from the uploaded-images bucket.
Create service account and manage roles
To create a service account for the delete-image trigger, and grant it the necessary permissions, in Cloud Shell, run the following command:
export DELETE_TRIGGER_SA=delete-image-trigger-sa export DELETE_SERVICE_REGION=us-west1 export DELETE_SERVICE=delete-image gcloud iam service-accounts create ${DELETE_TRIGGER_SA} gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} \ --member "serviceAccount:${DELETE_TRIGGER_SA}@${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/eventarc.eventReceiver" gcloud run services add-iam-policy-binding ${DELETE_SERVICE} \ --region=${DELETE_SERVICE_REGION} \ --member="serviceAccount:${DELETE_TRIGGER_SA}@${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/run.invoker"These commands create a service account named delete-image-trigger-sa, and add permissions to receive events and invoke the delete-image service.
In the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu (), navigate to More Products > Integration Services > Eventarc > Triggers, and then click + Create Trigger.
Specify the following trigger settings:
| Property | Value | | --- | --- | | Name | image-delete-trigger | | Event provider | select Cloud Storage | | Event type | select google.cloud.storage.object.v1.deleted | | Bucket | click Browse, then select the uploaded-images bucket, and then click Select | | Service account | select the delete-image-trigger-sa service account | | Event destination | select Cloud Run | | Select a Cloud Run service | select delete-image | | Service URL path | / |
If you're told that Pub/Sub must be granted a role, click Grant.
Click Create.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Trigger a service to delete image files and metadata
Check my progress
Test image deletion
To list an image in the Cloud Storage buckets and the corresponding document in Firestore, run the following commands:
export UPLOAD_BUCKET=uploaded-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} export GENERATED_BUCKET=generated-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} export IMAGE_NAME=vegas.jpg echo "Listing of image in uploaded-images bucket:" gcloud storage ls gs://${UPLOAD_BUCKET}/${IMAGE_NAME} echo "Listing of image in generated-images bucket:" gcloud storage ls gs://${GENERATED_BUCKET}/${IMAGE_NAME} echo "Image document in Firestore:" curl -q -s -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" \ -X GET "https://firestore.googleapis.com/v1/projects/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}/databases/(default)/documents/images/${IMAGE_NAME}"These commands display the Cloud Storage and Firestore details for a single image. Next, we remove that image.
To delete an image in the uploaded-images bucket, run the following command:
export UPLOAD_BUCKET=uploaded-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} export IMAGE_NAME=vegas.jpg gcloud storage rm gs://${UPLOAD_BUCKET}/${IMAGE_NAME}Eventarc will detect the removed file and call the image-delete service, which removes the thumbnail and Firestore document.
To check whether the thumbnail and Firestore document have been removed, run the same commands you ran earlier:
export UPLOAD_BUCKET=uploaded-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} export GENERATED_BUCKET=generated-images-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} export IMAGE_NAME=vegas.jpg echo "Listing of image in uploaded-images bucket:" gcloud storage ls gs://${UPLOAD_BUCKET}/${IMAGE_NAME} echo "Listing of image in generated-images bucket:" gcloud storage ls gs://${GENERATED_BUCKET}/${IMAGE_NAME} echo "Image document in Firestore:" curl -q -s -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" -X GET "https://firestore.googleapis.com/v1/projects/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}/databases/(default)/documents/images/${IMAGE_NAME}"The items have been removed.
In the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu (), navigate to Cloud Run > Services, and then click delete-image.
Click Logs.
The logs for the delete-image service show that the thumbnail was deleted from the generated-images bucket, and the Firestore document was deleted from the database.
Solution of Lab
export REGION=

curl -LO raw.githubusercontent.com/Techcps/GSP-Short-Trick/master/Building%20Event-Driven%20Orchestration%20on%20Google%20Cloud/techcps.sh
sudo chmod +x techcps.sh
./techcps.sh