Table of Contents
Overview
Google Cloud Source Repositories provides Git version control to support collaborative development of any application or service. In this lab, you will create a local Git repository that contains a sample file, add a Google Source Repository as a remote, and push the contents of the local repository. You will use the source browser included in Source Repositories to view your repository files from within the Cloud Console.
Objectives
In this lab, you will learn how to perform the following tasks:
Create a new repository
Add a Google Source Repository as a remote
Push to the Cloud Source Repository
Task 1. Create a new repository
- Start a new session in Cloud Shell and run the following command to create a new Cloud Source Repository named
REPO_DEMO:
gcloud source repos create REPO_DEMO
Copied!content_copy
You can safely ignore any billing warnings for creating repositories.
Test Completed Task
Click Check my progress to verify your performed task. If you have created a new repository you will see an assessment score.
Create a new repository
Check my progress
Task 2. Clone the new repository into your Cloud Shell session
- Clone the contents of your new Cloud Source Repository to a local repo in your Cloud Shell session:
gcloud source repos clone REPO_DEMO
The gcloud source repos clone command adds Cloud Source Repositories as a remote named origin and clones it into a local Git repository.
Task 3. Push to the Cloud Source Repository
- Go into the local repository you created:
cd REPO_DEMO
- Run the following command to create a file
myfile.txtin your local repository:
echo 'Hello World!' > myfile.txt
- Commit the file using the following Git commands:
git config --global user.email "you@example.com"
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git add myfile.txt
git commit -m "First file using Cloud Source Repositories" myfile.txt
Your output should resemble the following:
[master (root-commit) c072ab6] First file using Cloud Source Repositories
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 myfile.txt
- Once you've committed code to the local repository, add its contents to Cloud Source Repositories using the
git pushcommand:
git push origin master
- Git pushes the sample application files from the
masterbranch to theoriginremote:
Enumerating objects: 3, done.
Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 247 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
To https://source.developers.google.com/p/qwiklabs-gcp-ba5b4dcd/r/REPO_DEMO
* [new branch] master -> master
Task 4. Browse files in the Google Cloud Source Repository
Use the Google Cloud Source Repositories source code browser to view repository files. You can filter your view to focus on a specific branch, tag, or comment.
- Run the command to list the Repositories:
gcloud source repos list
Click on the URL to browse the sample files you pushed to the repository. The console shows the files in the master branch at the most recent commit.
Task 5. View a file in the Google Cloud repository
From the Console, open the Navigation menu () > View All Products. Under CI/CD section, click Source Repositories.
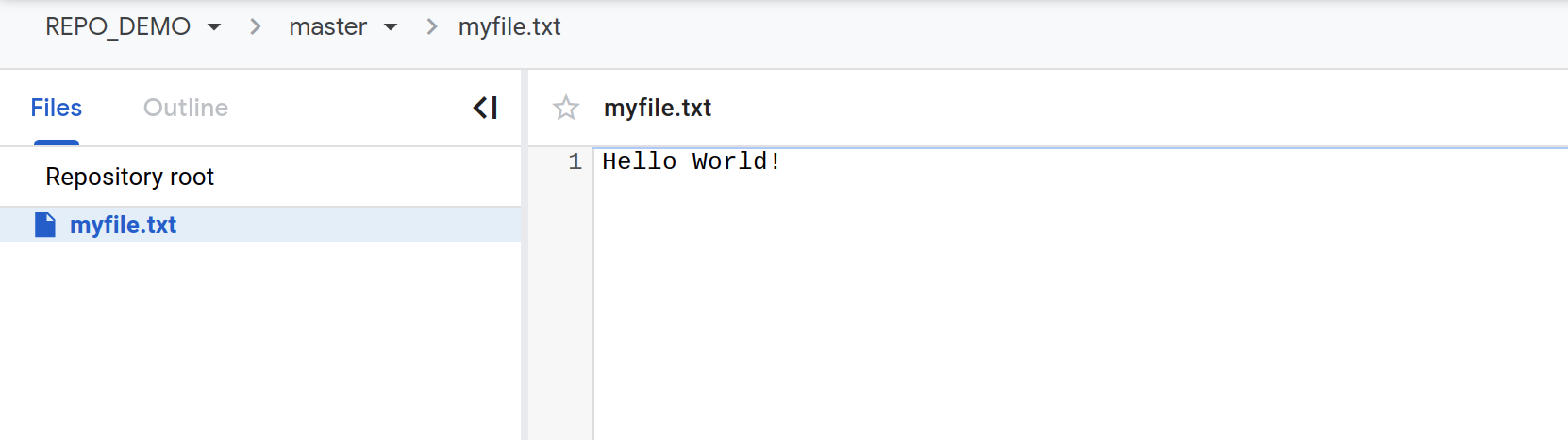
Click
REPO_DEMO>myfile.txtto view the file's contents in the source code browser.
Task 6. Test your understanding
Below are multiple-choice questions to reinforce your understanding of this lab's concepts. Answer them to the best of your abilities.
You can add content to Cloud Source Repositories using the ____ command.
git push
git commit
git clone
The gcloud source repos clone command adds Cloud Source Repositories as a remote named origin.
True
False
Solution of Lab
curl -LO raw.githubusercontent.com/Techcps/GSP-Short-Trick/master/Cloud%20Source%20Repositories%3A%20Qwik%20Start/techcpsgsp121.sh
sudo chmod +x techcpsgsp121.sh
./techcpsgsp121.sh