Table of Contents
Overview
Cloud Run is a fully managed compute platform that allows you to run stateless containers that are invocable with HTTP requests. You can deploy code written in any programming language on Cloud Run if you can build a container image from it. You can use the source-based deployment option that builds the container for you when developing your application in Go, Node.js, Python, Java, .NET Core, or Ruby.
Cloud Run is serverless, and runs your containers on Google's scalable infrastructure. It's built on Knative, and lets you choose to run your containers either fully managed with Cloud Run, or in your Google Kubernetes Engine cluster with Cloud Run on GKE.
Cloud Run works well with other services on Google Cloud, so you can build full-featured applications without spending too much time operating, configuring, and scaling your Cloud Run service.
Objectives
In this lab, you:
Use Cloud Build to create a Docker container image for your application.
Deploy the container image to Cloud Run.
Run and test the containerized application.
Setup
For each lab, you get a new Google Cloud project and set of resources for a fixed time at no cost.
Sign in to Qwiklabs using an incognito window.
Note the lab's access time (for example,
1:15:00), and make sure you can finish within that time.
There is no pause feature. You can restart if needed, but you have to start at the beginning.When ready, click Start lab.
Note your lab credentials (Username and Password). You will use them to sign in to the Google Cloud Console.
Click Open Google Console.
Click Use another account and copy/paste credentials for this lab into the prompts.
If you use other credentials, you'll receive errors or incur charges.Accept the terms and skip the recovery resource page.
Activate Google Cloud Shell
Google Cloud Shell is a virtual machine that is loaded with development tools. It offers a persistent 5GB home directory and runs on the Google Cloud.
Google Cloud Shell provides command-line access to your Google Cloud resources.
In Cloud console, on the top right toolbar, click the Open Cloud Shell button.
Click Continue.
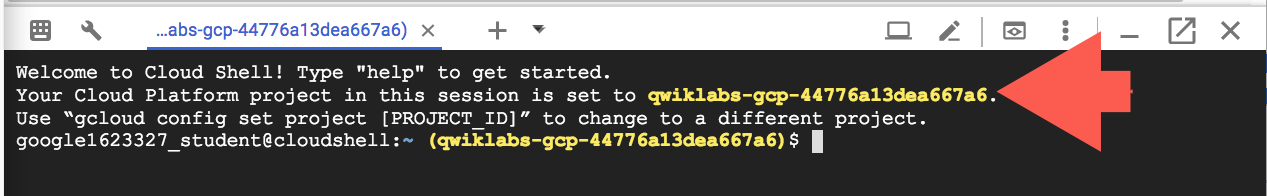
It takes a few moments to provision and connect to the environment. When you are connected, you are already authenticated, and the project is set to your PROJECT_ID. For example:
gcloud is the command-line tool for Google Cloud. It comes pre-installed on Cloud Shell and supports tab-completion.
- You can list the active account name with this command:
gcloud auth list
Output:
Credentialed accounts:
- @.com (active)
Example output:
Credentialed accounts:
- google1623327_student@qwiklabs.net
- You can list the project ID with this command:
gcloud config list project
Output:
[core]
project =
Example output:
[core]
project = qwiklabs-gcp-44776a13dea667a6
Note: Full documentation of gcloud is available in the gcloud CLI overview guide .
Task 1. Configure your project and environment
In this task, you set environment variables for your Cloud Shell environment, and enable the relevant Google APIs for use in this lab.
Sign in to the Google Cloud console with your lab credentials, and open the Cloud Shell terminal window.
To set your project ID and region environment variables, in Cloud Shell, run the following commands:
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project) REGION=us-east4To enable relevant APIs, run the following command:
gcloud services enable artifactregistry.googleapis.com \ cloudbuild.googleapis.com \ run.googleapis.com
To verify the objective, click Check my progress.
Enable relevant APIs.
Check my progress
Task 2. Test the application locally
In this task, you copy a sample Node.js application. Then, you build and run it locally in your Cloud Shell environment.
Copy the application
Create an
appdirectory, and make it the current working directory:mkdir app && cd appTo copy the app from Cloud Storage, and extract it's files, execute the following command:
gsutil cp gs://cloud-training/CBL515/sample-apps/sample-node-app.zip . && unzip sample-node-app
Install application dependencies
Change to the app directory:
cd sample-node-appTo view the application source code, view the contents of the
server.jsfile in the top-level directory:cat server.jsThis is the main application entry point. This sample application is a basic retail service that provides an API that returns product data when requests are made to the application over HTTP.
To install the app's dependency modules locally, execute the following command:
npm install
Test the application
To run the app locally, execute the following command:
npm startYou should see the following output:
> sample-node-app@1.0.0 start > node server.js Sample-node-app listening on port 8080!To open a second Cloud Shell terminal window, in the Cloud Shell navigation bar, click ().
Test the sample API by making a few HTTP requests to the application:
curl http://localhost:8080/service/products | jqWe use the command line tool jq to parse and format the JSON response from the application.
The application should respond with a list of products:
[ { "id": "1YMWWN1N4O", "name": "Home Barista Kit", "description": "Always wanted to brew coffee with Chemex and Aeropress at home?", "picture": "static/img/products/barista-kit.jpg", "cost": 124, "categories": [ "cookware" ] }, { "id": "L9ECAV7KIM", "name": "Terrarium", "description": "This terrarium will look great in your white painted living room.", "picture": "static/img/products/terrarium.jpg", "cost": 36.45, "categories": [ "gardening" ] }, { "id": "2ZYFJ3GM2N", "name": "Film Camera", "description": "This camera looks like it's a film camera, but it's actually digital.", "picture": "static/img/products/film-camera.jpg", "cost": 2245, "categories": [ "photography", "vintage" ] }, { "id": "LS4PSXUNUM", "name": "Metal Camping Mug", "description": "You probably don't go camping that often but this is better than plastic cups.", "picture": "static/img/products/camp-mug.jpg", "cost": 24.33, "categories": [ "cookware" ] }, { "id": "9SIQT8TOJO", "name": "City Bike", "description": "This single-gear bike probably cannot climb the hills of San Francisco.", "picture": "static/img/products/city-bike.jpg", "cost": 789.5, "categories": [ "cycling" ] }, { "id": "6E92ZMYYFZ", "name": "Air Plant", "description": "Have you ever wondered whether air plants need water? Buy one and figure out.", "picture": "static/img/products/air-plant.jpg", "cost": 12.3, "categories": [ "gardening" ] } ]Make a second API request to fetch a specific product by ID:
curl http://localhost:8080/service/products/1YMWWN1N4O | jqThe application should respond with details about the specific product:
{ "id": "1YMWWN1N4O", "name": "Home Barista Kit", "description": "Always wanted to brew coffee with Chemex and Aeropress at home?", "picture": "static/img/products/barista-kit.jpg", "cost": 124, "categories": [ "cookware" ] }To exit the application, in the first Cloud Shell terminal window, type Ctrl+C.
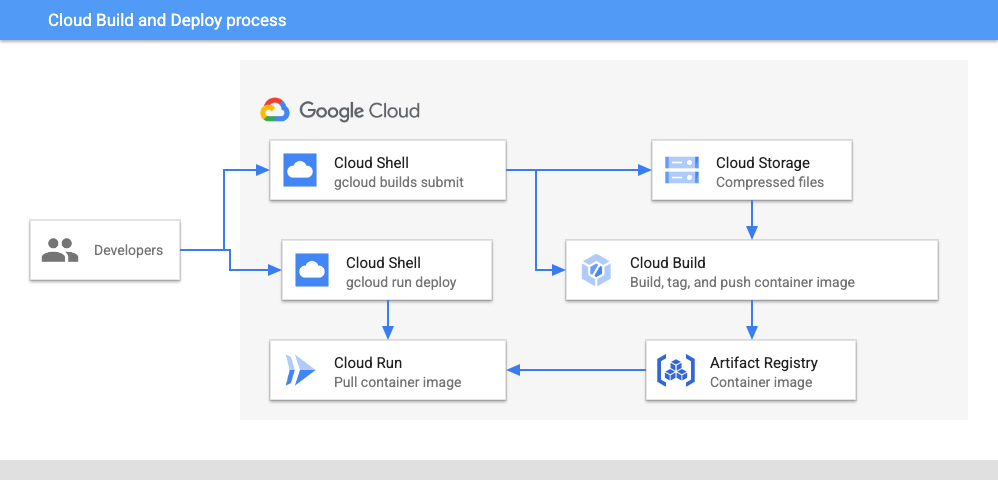
Task 3. Containerize the application with Cloud Build
Cloud Build is a service that executes your builds on Google Cloud. With Cloud Build, you can continuously build, test, and deploy your application by using a continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipeline.
To provide instructions to Cloud Build, you create a build configuration file that contains a set of tasks. These instructions can configure builds to fetch dependencies, run unit and integration tests, perform static analysis, and create artifacts with build tools like docker, gradle, maven, and others.
In this task, you use Cloud Build to build a Docker container for your application, and push the resulting container image to a repository in Artifact Registry.
Create the repository
On the Google Cloud console title bar, in the Search field, type Artifact Registry, click Search, and then click Artifact Registry.
Click the ( Pin) next to Artifact Registry.
Click Create Repository.
In the Create repository page, provide the following information, and leave the remaining settings as their defaults:
Name
my-repo
Format
Docker
Location type
Region
Region
us-east4Click Create, and wait for the repository to be created.
Authenticate Docker to use the repository
Before you can push images to the repository, you must configure Docker to authenticate requests to the repository in Artifact Registry.
To set up authentication to Docker repositories in the region
us-east4, in Cloud Shell, run the following command:gcloud auth configure-docker ${REGION}-docker.pkg.devWhen prompted, type Y.
Create the build configuration file
To provide instructions to Cloud Build, you create a build configuration file that contains a set of tasks. These instructions can configure builds to fetch dependencies, run unit and integration tests, perform static analysis, and create artifacts with builders like docker, gradle, maven, and others.
Set an environment variable for the repository name:
REPO=${REGION}-docker.pkg.dev/${PROJECT_ID}/my-repoCreate the build configuration file:
cat > cloudbuild.yaml <<EOF steps: - name: 'gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker' args: [ 'build', '-t', '${REPO}/sample-node-app-image', '.' ] images: - '${REPO}/sample-node-app-image' EOFView the
cloudbuild.yamlfile:cat cloudbuild.yamlThe build step builds a container image by using the docker builder from source code and the Dockerfile which are located in the current directory. The built image is then pushed to the repository in Artifact Registry.
Build the container
To build the container with Cloud Build, execute the following command:
gcloud builds submit --region=$REGION --config=cloudbuild.yamlHere's similar (partial) output from the command:
... ... b3389e626b47: Pushed 38610c0cfc18: Pushed latest: digest: sha256:b6007afa5e8fb05d8ac617ddf5fee8d58cc6ba8901038c97f8e360520c5fdbf4 size: 3051 DONE ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ID: f803a828-dc50-41cb-bc94-71dfb8c83648 CREATE_TIME: 2023-02-28T18:28:41+00:00 DURATION: 1M23S SOURCE: gs://qwiklabs-gcp-02-26de4317fac8_cloudbuild/source/1677608919.352478-c157fa4ae8544b3dbba23b5f29145286.tgz IMAGES: asia-east1-docker.pkg.dev/qwiklabs-gcp-02-26de4317fac8/my-repo/sample-node-app-image (+1 more) STATUS: SUCCESSCloud Build first uploads your application source code and other files from the specified directory to Cloud Storage. It then builds the container image that contains your application from the instructions specified in the build configuration and Dockerfile, tags the image with the specified image name, and pushes the image to the repository in Artifact Registry.
View build history
On the Google Cloud console title bar, in the Search field, type Cloud Build, click Search, and then click Cloud Build.
For Region, select
us-east4.Click the build ID for the build at the top of the list.
The details of the build, including the build log, are displayed.
View the container image in Artifact Registry
After the build command completes, in the Google Cloud console, in the navigation menu (), click Artifact Registry > Repositories.
Click the my-repo repository to display the sample-node-app-image container image.
To verify the objective, click Check my progress.
Build a container image with Cloud Build.
Check my progress
Task 4. Deploy the container to Cloud Run
With the container image built, you can now deploy it to Cloud Run. There are two approaches for deploying to Cloud Run:
Managed Cloud Run: A fully managed service model where the entire container lifecycle is managed by Cloud Run. You use this approach in this lab.
Cloud Run on Anthos: Cloud Run with an extra layer of control, which lets you bring your own clusters and pods from GKE.
In this task, you deploy your container image to the fully managed Cloud Run service on Google Cloud.
To deploy the container image, in Cloud Shell, execute the following command:
gcloud run deploy sample-node-app --image ${REPO}/sample-node-app-image --region $REGION --allow-unauthenticatedThe allow-unauthenticated option enables access to the service without requiring any authentication.
After the command completes, in the Google Cloud console, in the navigation menu () click Cloud Run.
To display the details of the Cloud Run service, click the sample-node-app service name.
To verify the objective, Click Check my progress.
Deploy the container image to Cloud Run.
Check my progress
Task 5. Test the application on Cloud Run
To verify that the service is running, and available to accept requests, in Cloud Shell, execute the following command:
gcloud run services listThe output of the command is similar to:
✔ SERVICE: sample-node-app REGION: asia-east1 URL: https://sample-node-app-dduno3adrq-uc.a.run.app LAST DEPLOYED BY: student-04-329a97f025fd@qwiklabs.net LAST DEPLOYED AT: 2023-02-28T22:21:04.803928ZFrom the command output, copy the value of the URL, and paste it in the curl command appending
service/productsto the end of the URL as shown. Pipe the output to thejqcommand, and press ENTER:curl https://sample-node-app-dduno3adrq-uc.a.run.app/service/products | jqThe output should be similar to that received from the application when you run it locally in an earlier task.
To verify the objective, click Check my progress.
Solution of Lab
export REGION=

curl -LO raw.githubusercontent.com/quiccklabs/Labs_solutions/master/Deploying%20a%20Containerized%20Application%20on%20Cloud%20Run/quicklab.sh
sudo chmod +x quicklab.sh
./quicklab.sh