Overview
In this lab, you use the Google Cloud Console to build GKE Autopilot clusters and deploy a sample Pod.
Objectives
In this lab, you learn how to perform the following tasks:
Use the Google Cloud Console to build and manipulate GKE Autopilot clusters
Use the Google Cloud Console to deploy a Pod
Use the Google Cloud Console to examine the cluster and Pods
Lab setup
For each lab, you get a new Google Cloud project and set of resources for a fixed time at no cost.
Sign in to Qwiklabs using an incognito window.
Note the lab's access time (for example,
1:15:00), and make sure you can finish within that time.
There is no pause feature. You can restart if needed, but you have to start at the beginning.When ready, click Start lab.
Note your lab credentials (Username and Password). You will use them to sign in to the Google Cloud Console.
Click Open Google Console.
Click Use another account and copy/paste credentials for this lab into the prompts.
If you use other credentials, you'll receive errors or incur charges.Accept the terms and skip the recovery resource page.
After you complete the initial sign-in steps, the project dashboard opens.
Task 1. Deploy GKE clusters
In this task, you use the Google Cloud Console and Cloud Shell to deploy GKE clusters.
Use the Google Cloud Console to deploy a GKE cluster
In the Google Cloud Console, on the Navigation menu (), click Kubernetes Engine > Clusters.
Click Create to begin creating a GKE cluster.
Examine the console UI and the controls to change the cluster name, the cluster location, the Kubernetes version, the number of nodes, and the node resources such as the machine type in the default node pool.
Clusters can be created across a region or in a single zone. A single zone is the default. When you deploy across a region the nodes are deployed to three separate zones and the total number of nodes deployed will be three times higher.
- Change the cluster name to autopilot-cluster-1 and region to
us-east1. Leave all the values at their defaults and click Create.
The cluster begins provisioning.
Note: You need to wait a few minutes for the cluster deployment to complete.
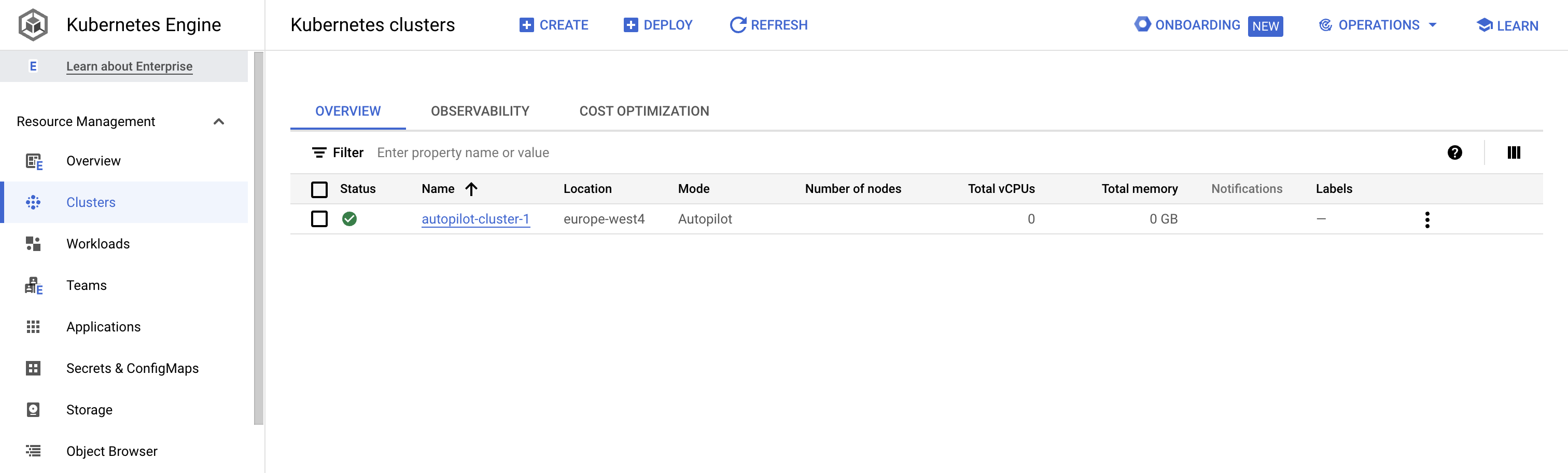
When provisioning is complete, the Kubernetes Engine > Clusters page looks like this screenshot:
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Assessment Completed!
Deploy GKE cluster
Check my progress
Assessment Completed!
Click the cluster name autopilot-cluster-1 to view the cluster details.
You can scroll down the page to view more details.
Click the Storage tab under the cluster name (autopilot-cluster-1) at the top to view more of the cluster details.
Task 2. Deploy a sample workload
In this task, you will use the Google Cloud console to deploy a Pod running the nginx web server as a sample workload.
In the Google Cloud Console, on the Navigation menu(), click Kubernetes Engine > Workloads.
Click Create deployment.
For Deployment name enter nginx-1.
Accept the default container image, nginx:latest, which deploys three Pods each with a single container running the latest version of nginx.
Click the Deploy button, leaving the Configuration details at the defaults.
When the deployment completes your screen will refresh to show the details of your new nginx deployment.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Deploy a sample nginx workload
Check my progress
Task 3. View details about workloads in the Google Cloud Console
In this task, you view details about your GKE workloads directly in the Google Cloud Console.
In the Google Cloud Console, on the Navigation menu (
), click Kubernetes Engine > Workloads.
In the Google Cloud Console, on the Kubernetes Engine > Workloads page, click nginx-1.
This displays the overview information for the workload, showing details like resource utilization charts, links to logs, and details of the Pods associated with this workload.
In the Google Cloud Console, click the Details tab for the nginx-1 workload. The Details tab shows more details about the workload including the Pod specification, number and status of Pod replicas, and details about the horizontal Pod autoscaler.
Click the Revision History tab. This displays a list of the revisions that have been made to this workload.
Click the Events tab. This tab lists events associated with this workload.
Then, click the YAML tab. This tab provides the complete YAML file that defines these components and full configuration of this sample workload.
While you are still in the Google Cloud Console's Details tab for the nginx-1 workload, click the Overview tab, scroll down to the Managed Pods section, and click the name of one of the Pods to view the details page for that Pod.
The Pod details page provides information on the Pod configuration and resource utilization and the node where the Pod is running.
In the Pod details page, you can click the Events and Logs tabs to view event details and links to container logs in Cloud Operations.
Click the YAML tab to view the detailed YAML file for the Pod configuration.