In this article, I will introduce the simplest integration of real-time, after much learning and optimization in the most effective way.
Technologies used in the article:
I will skip the steps to install Laravel + VueJS and to register Pusher, you can learn how to set up the paths I quoted above.
#Fontend VueJS
I will guide the setup on the front end VueJS side. Install the support package from the pusher + Laravel echo side provided.
npm install --save laravel-echo pusher-js
Here I install a package named vue-echo .
npm install vue-echo-laravel --save
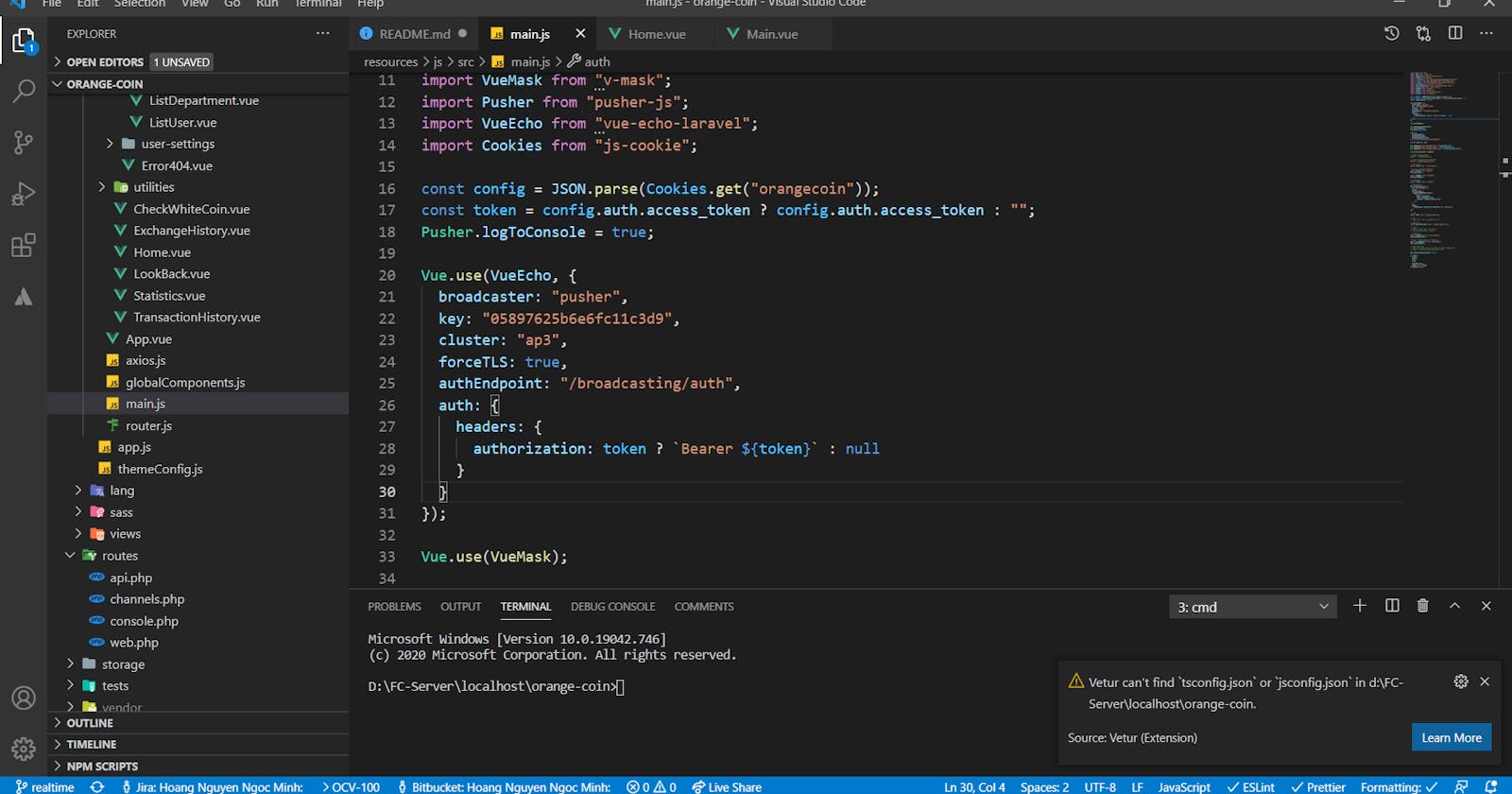
Next add the below configs to the main.js, app.js or bootstrap.js file (depending on your file).
import Pusher from "pusher-js";
import VueEcho from "vue-echo-laravel";
// Enable pusher logging - don't include this in production
Pusher.logToConsole = true;
Vue.use(VueEcho, {
broadcaster: "pusher",
key: "xxxxxxxxxxxxx",
cluster: "ap3",
forceTLS: true,
authEndpoint: "/broadcasting/auth",
auth: {
headers: {
// authorization: token ? `Bearer ${token}` : null // Enabled - If you are using Bearer for authentication
}
}
});
This is the content I added to my project
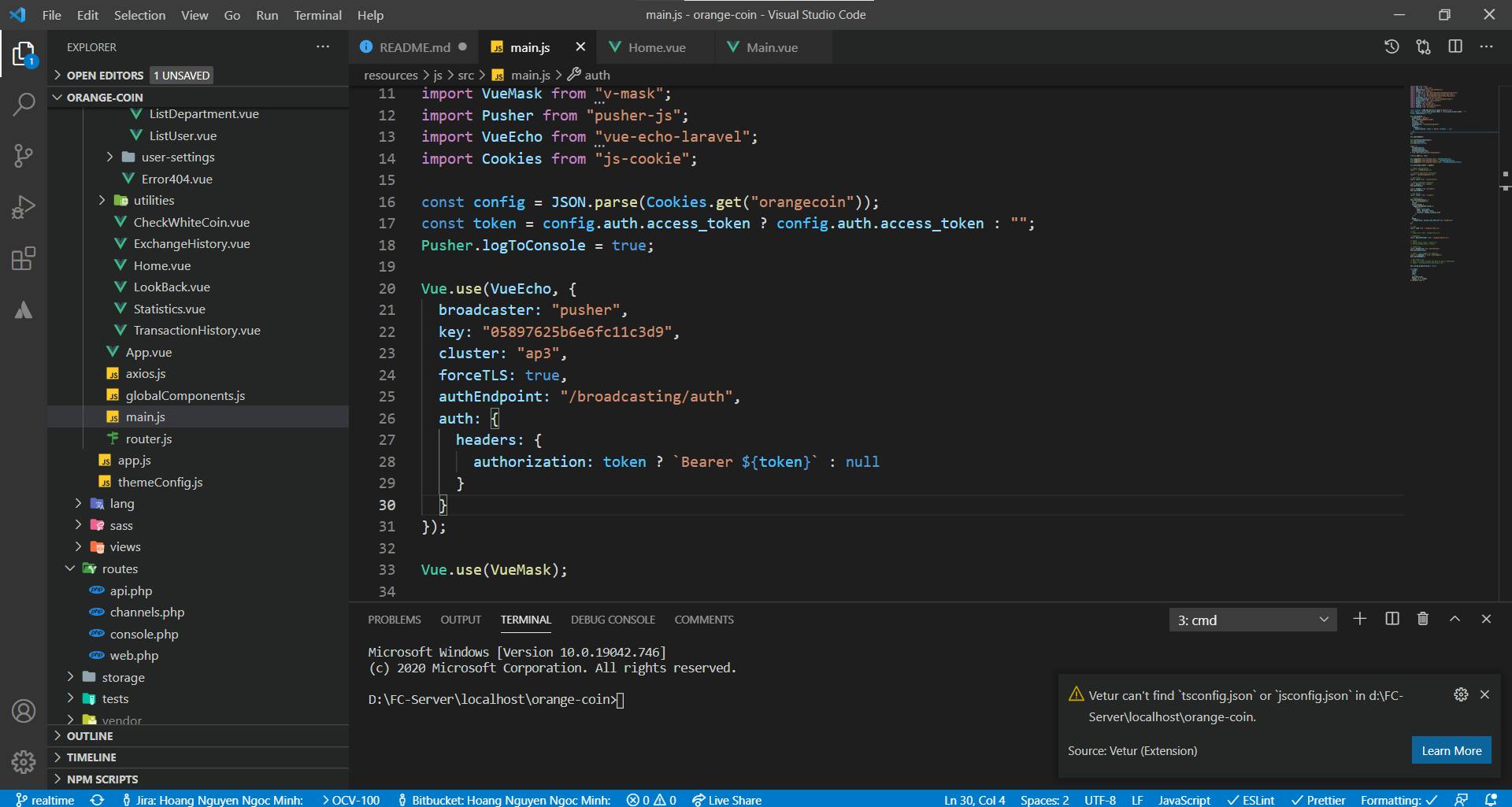
Once vue-echo is registered, every Vue instance is able to subscribe to channels and listen to events through the this.$echo property on the connection you specified earlier.
var vm = new Vue({
mounted() {
// Listen for the 'NewMessageNotification' event in the 'synchronized' private channel
this.$echo.private('synchronized').listen('NewMessageNotification', (payload) => {
console.log(payload);
});
}
});
This is the content I added to my project
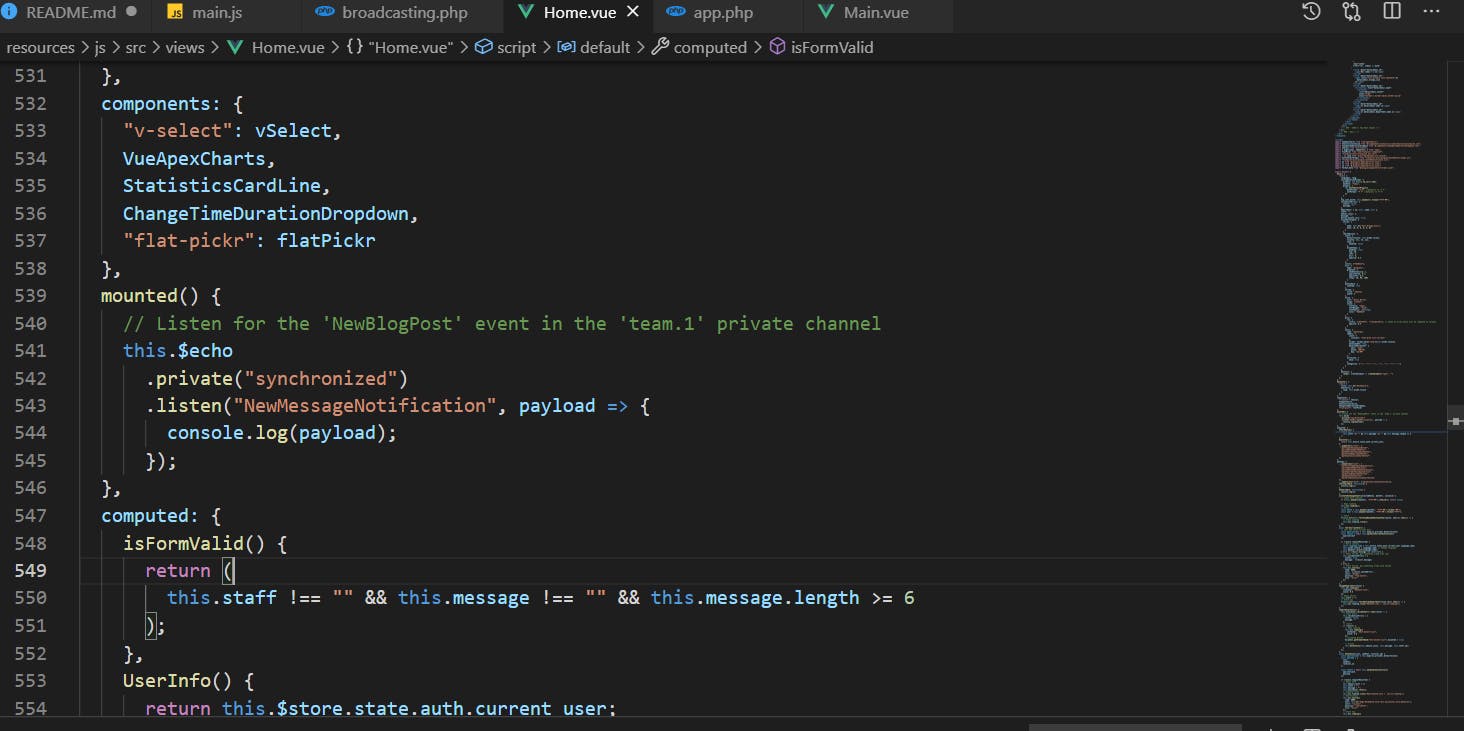
#Backend Laravel
Terminal
composer require pusher/pusher-php-server
At config/app.php you need to unhide or add this line
App\Providers\BroadcastServiceProvider::class
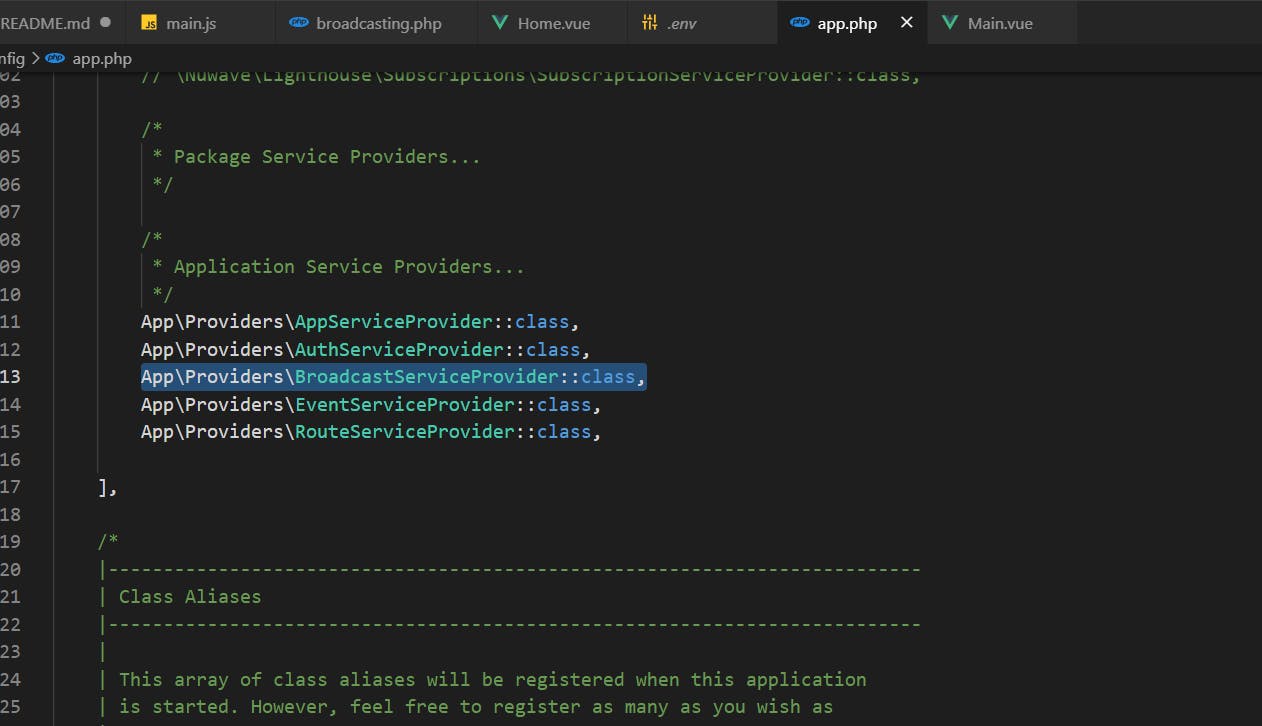
Finally, you will need to change your broadcast driver to pusher in your .env file:
PUSHER_APP_ID=xxxxxxxx
PUSHER_APP_KEY=xxxxxxxxxx
PUSHER_APP_SECRET=xxxxxxxxxxx
PUSHER_APP_CLUSTER=xxxxxx
BROADCAST_DRIVER=pusher
CACHE_DRIVER=file
QUEUE_CONNECTION=sync
SESSION_DRIVER=file
SESSION_LIFETIME=120
#Create Event - From Backend
I will quickly create an Events named NewMessageNotification at app\Events
<?php
namespace App\Events;
use Illuminate\Broadcasting\Channel;
use Illuminate\Broadcasting\InteractsWithSockets;
use Illuminate\Broadcasting\PresenceChannel;
use Illuminate\Broadcasting\PrivateChannel;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Broadcasting\ShouldBroadcast;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Events\Dispatchable;
use Illuminate\Queue\SerializesModels;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Broadcasting\ShouldBroadcastNow;
class NewMessageNotification implements ShouldBroadcastNow
{
use Dispatchable, InteractsWithSockets, SerializesModels;
public $message;
/**
* Create a new event instance.
*
* @return void
*/
public function __construct($message)
{
$this->message = $message;
}
/**
* Get the channels the event should broadcast on.
*
* @return \Illuminate\Broadcasting\Channel|array
*/
public function broadcastOn()
{
return new PrivateChannel('synchronized');
}
}
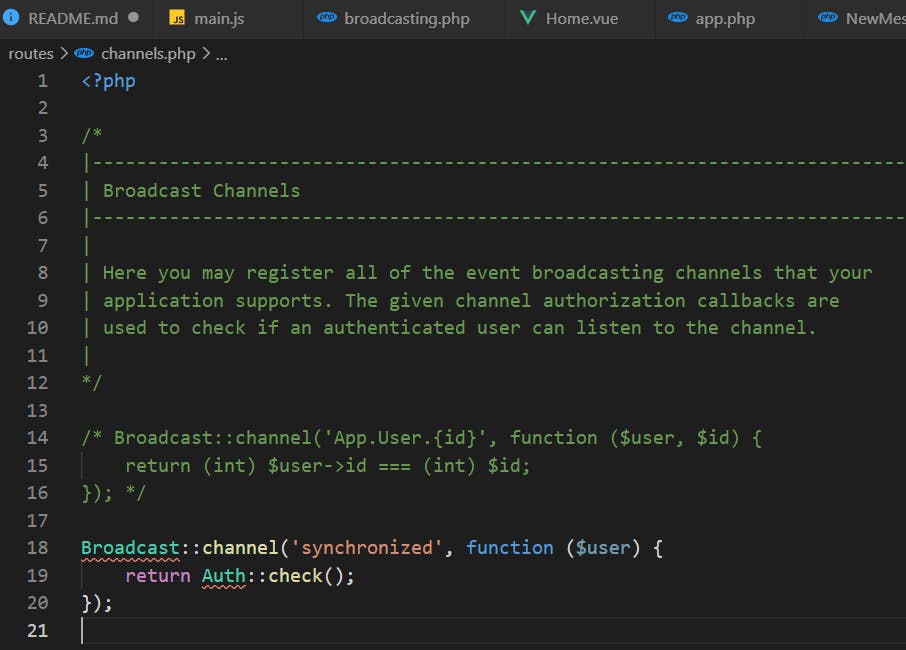
Register channels at routes/channels.php withreturn Auth::check(); . I force the Client-side to log in to listen to the event.
Broadcast::channel('synchronized', function ($user) {
return Auth::check();
});
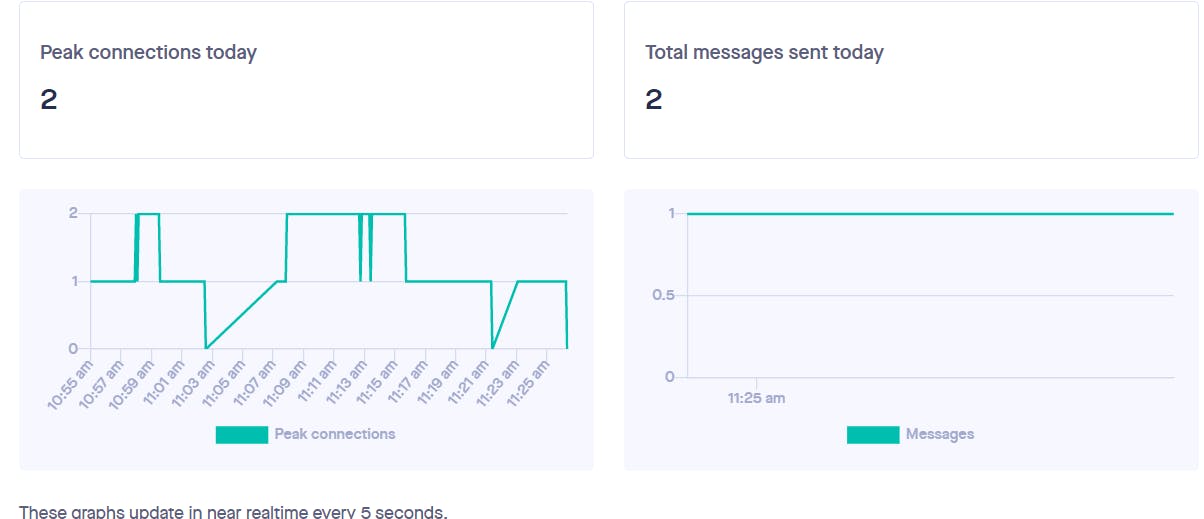
Check the dashboard in Pusher, if a successful connection will be displayed.
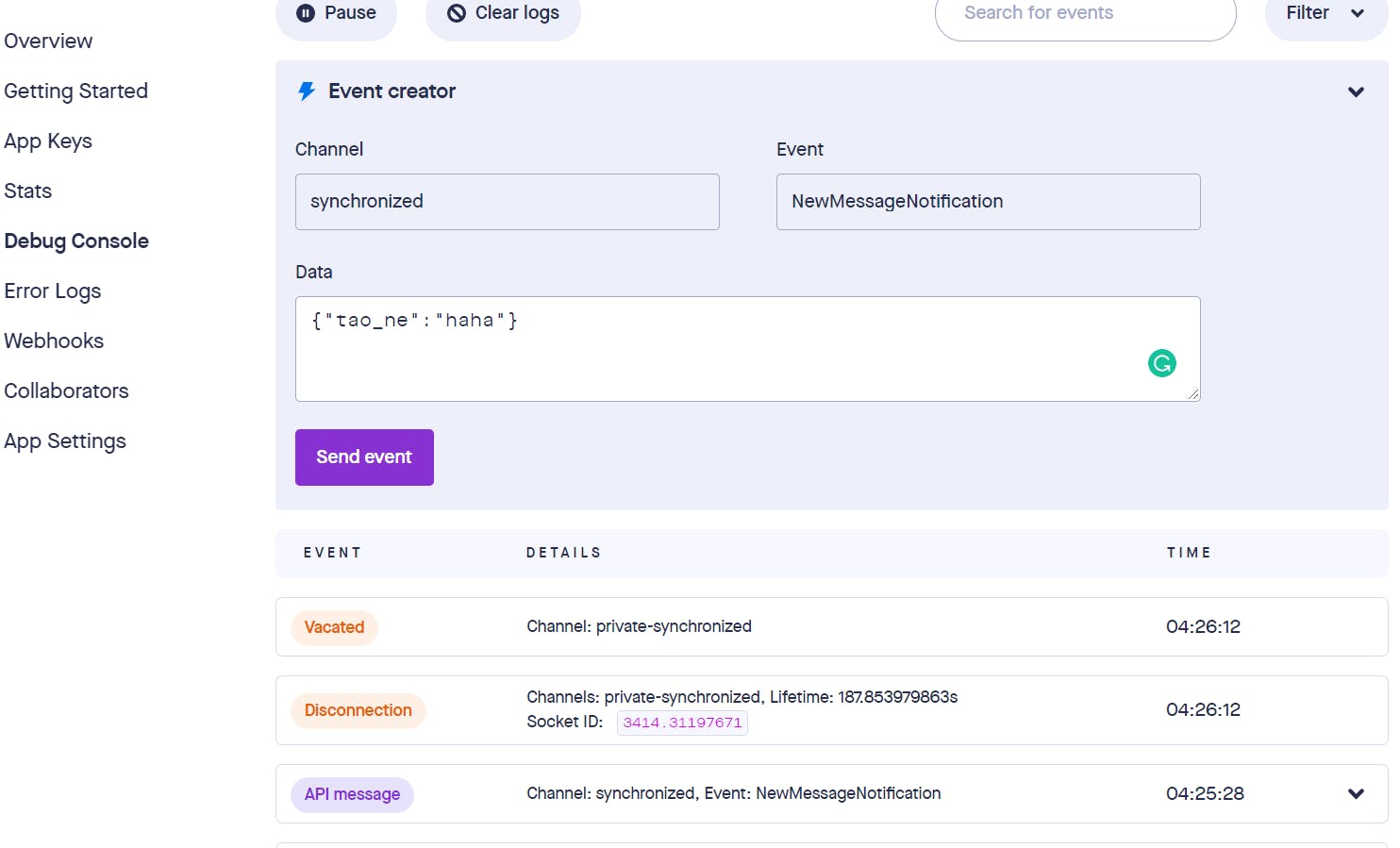
I'm going to use the Debug console function in Pusher to do the event quick send.
Or you can also use the Laravel Backend to post events, I will guide you in the following post, or refer here.
And this is the result
Have any questions, please comment below. Good luck.